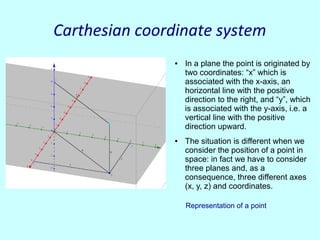
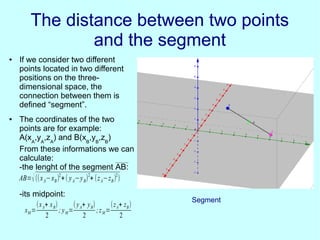
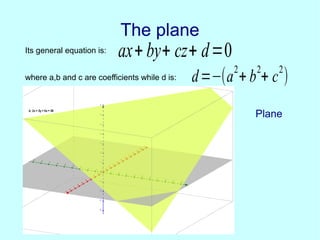
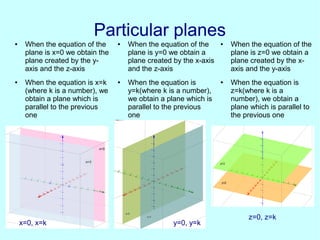
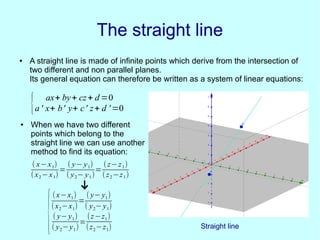
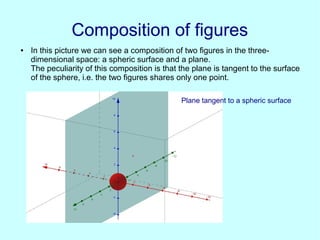
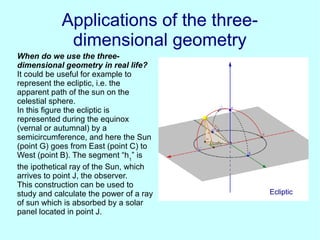
This document discusses analytic geometry in three dimensions. It begins by explaining the Cartesian coordinate system in three dimensions, using three axes (x, y, z) to locate a point in space. It then discusses how to calculate the distance and midpoint between two points. Next, it covers planes and their general and particular equations. It also discusses properties of planes like parallelism and perpendicularity. The document continues by defining straight lines and spheres, and provides their equations. It concludes by showing an example of a plane tangent to a sphere and discusses applications of three-dimensional geometry like representing the ecliptic.