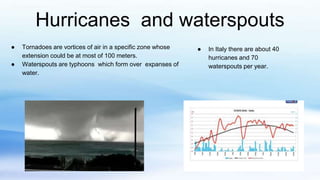
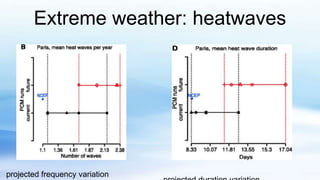
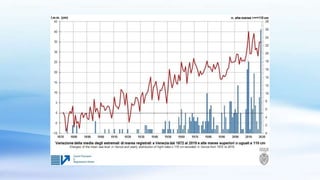
The document summarizes different types of extreme weather events that occur in Italy, including hurricanes, tornadoes, waterspouts, cloudbursts, heatwaves, droughts, severe storms, and floods. It provides statistics on hurricanes and waterspouts in Italy, describes the causes and impacts of these phenomena, and gives some examples of extreme weather events that have impacted Italy in recent years, such as heatwaves in 2019, drought conditions in 2017-2018, and storms and flooding in Venice. The document also discusses how climate change is exacerbating some of these extreme weather risks in Italy in the future.