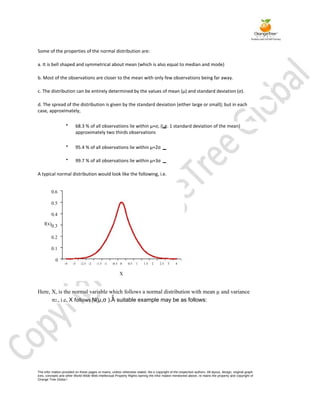
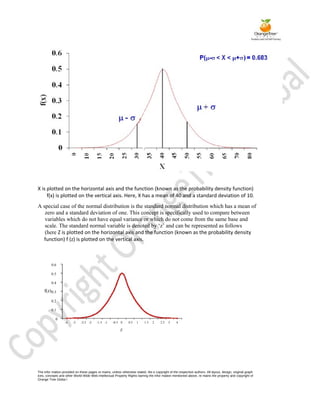
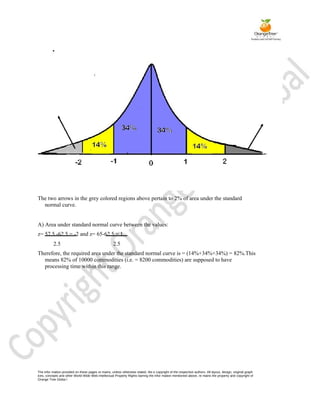
Probability refers to the likelihood of an event occurring. It can be expressed as a fraction between 0 and 1, with the total number of possible outcomes as the denominator and number of favorable outcomes as the numerator. A random variable is a value that can vary in an experiment but whose outcome is uncertain before the experiment. Probability distributions specify the probabilities of random variables taking on particular values. There are discrete and continuous probability distributions. Important discrete distributions include binomial and Poisson, while the normal distribution is the most important continuous distribution.