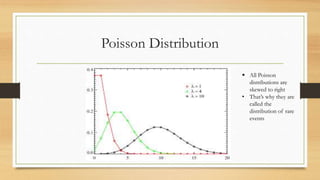
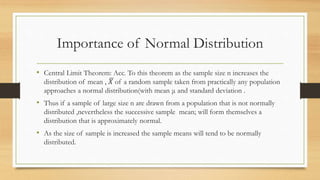
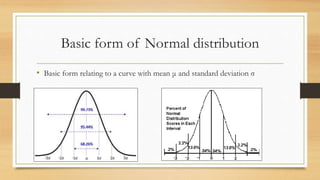
This document discusses different types of frequency distributions including theoretical, empirical, binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides details on the key characteristics of each distribution such as their assumptions, formulas, and appropriate uses. The normal distribution is described as the most useful theoretical distribution for continuous variables and an approximation of the binomial distribution for large sample sizes. Properties of the normal distribution include being bell-shaped and symmetrical with the mean, median, and mode all equal.












![• If we want to obtain the probable frequencies of the various outcomes in N
sets on n trials, the following expression shall be used:
• N(q+p)n= N[qn +nC1 qn-1.p+ nc2qn-2 p2+…+ nCr qn-rpr+…+pn]
• Mean of the binomial distribution= np
• Standard deviation= 𝑛𝑝𝑞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samplingdistribution-191106073608/85/Sampling-distribution-by-Dr-Ruchi-Jain-13-320.jpg)