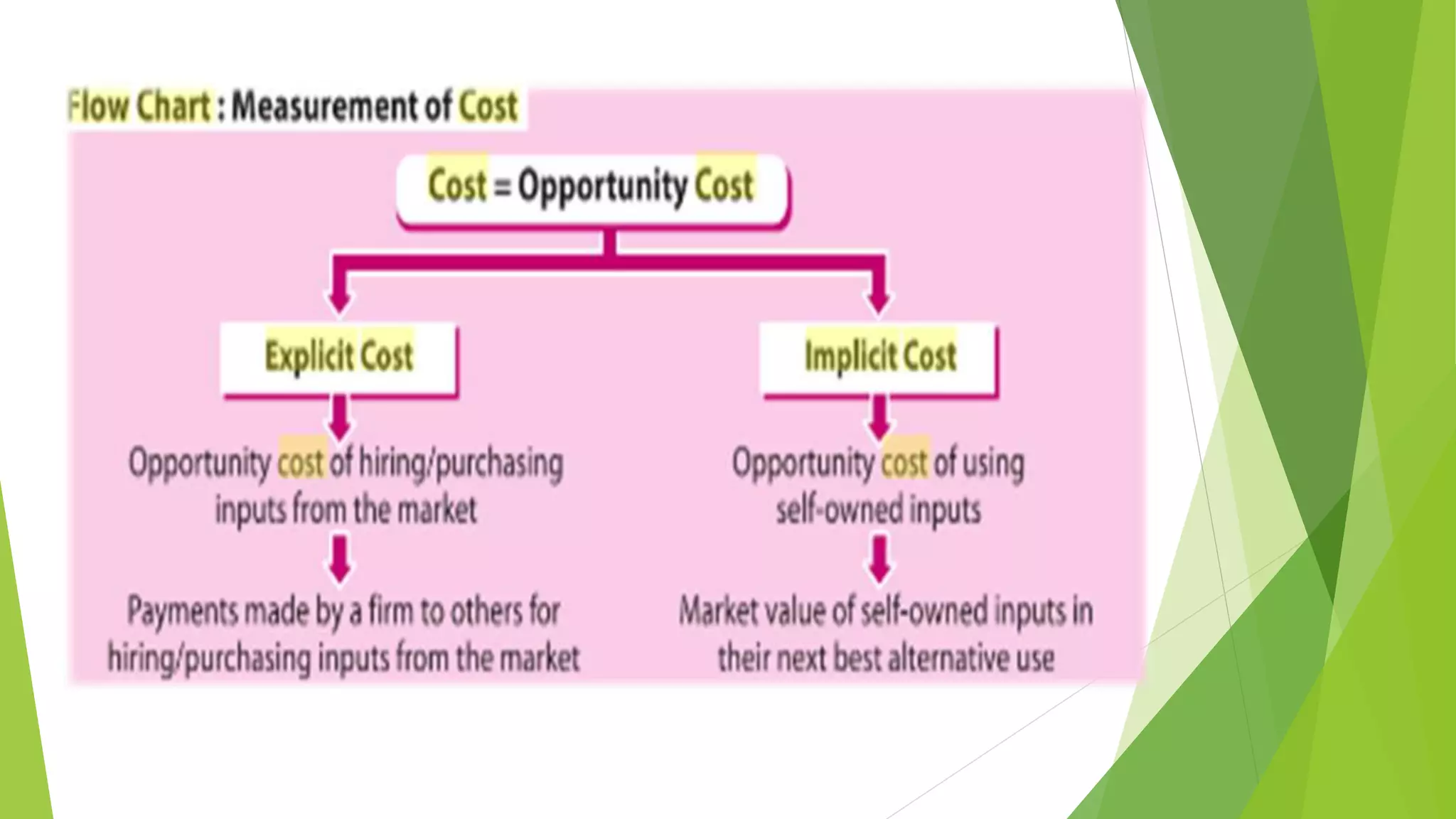
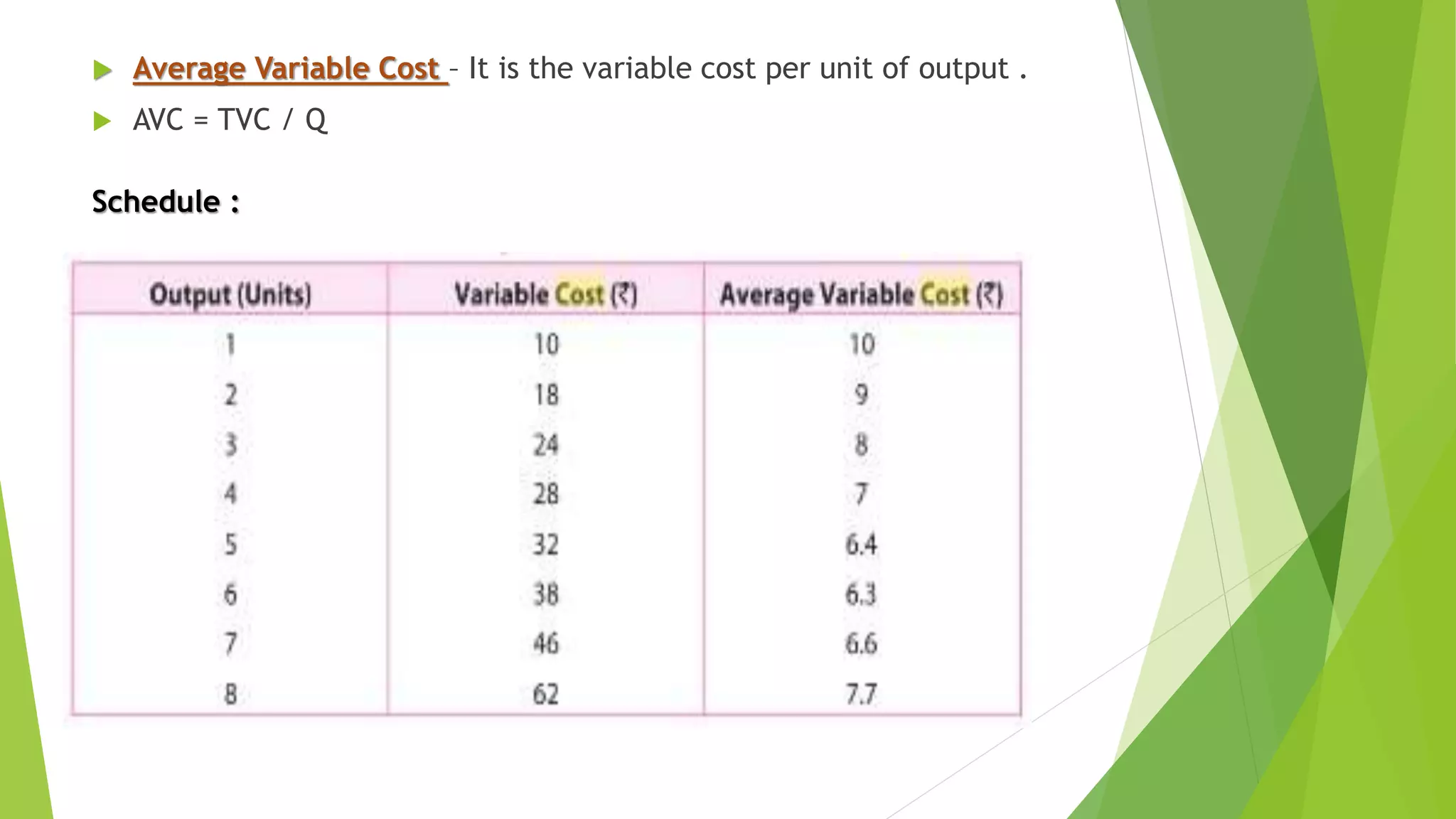
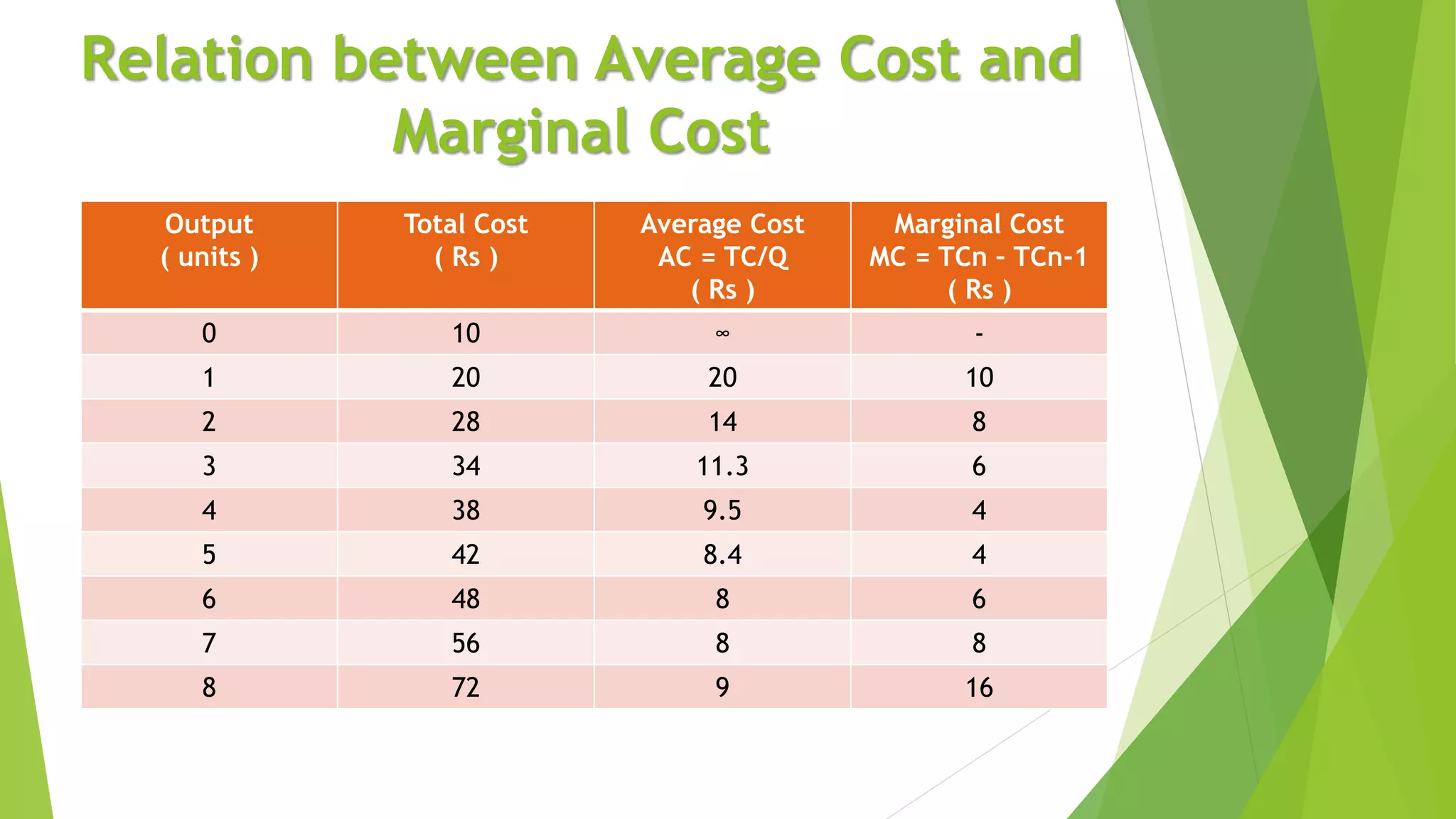
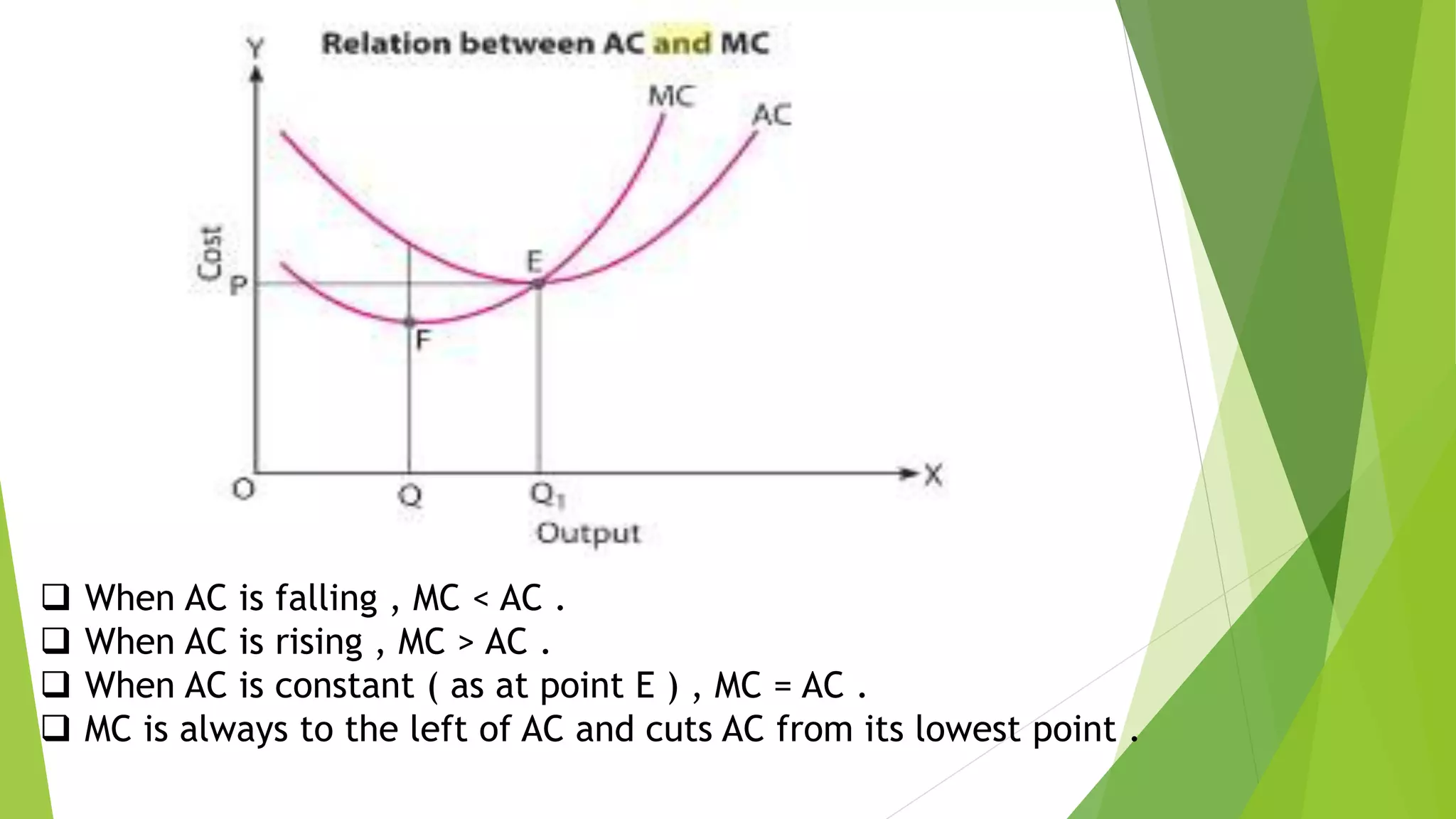
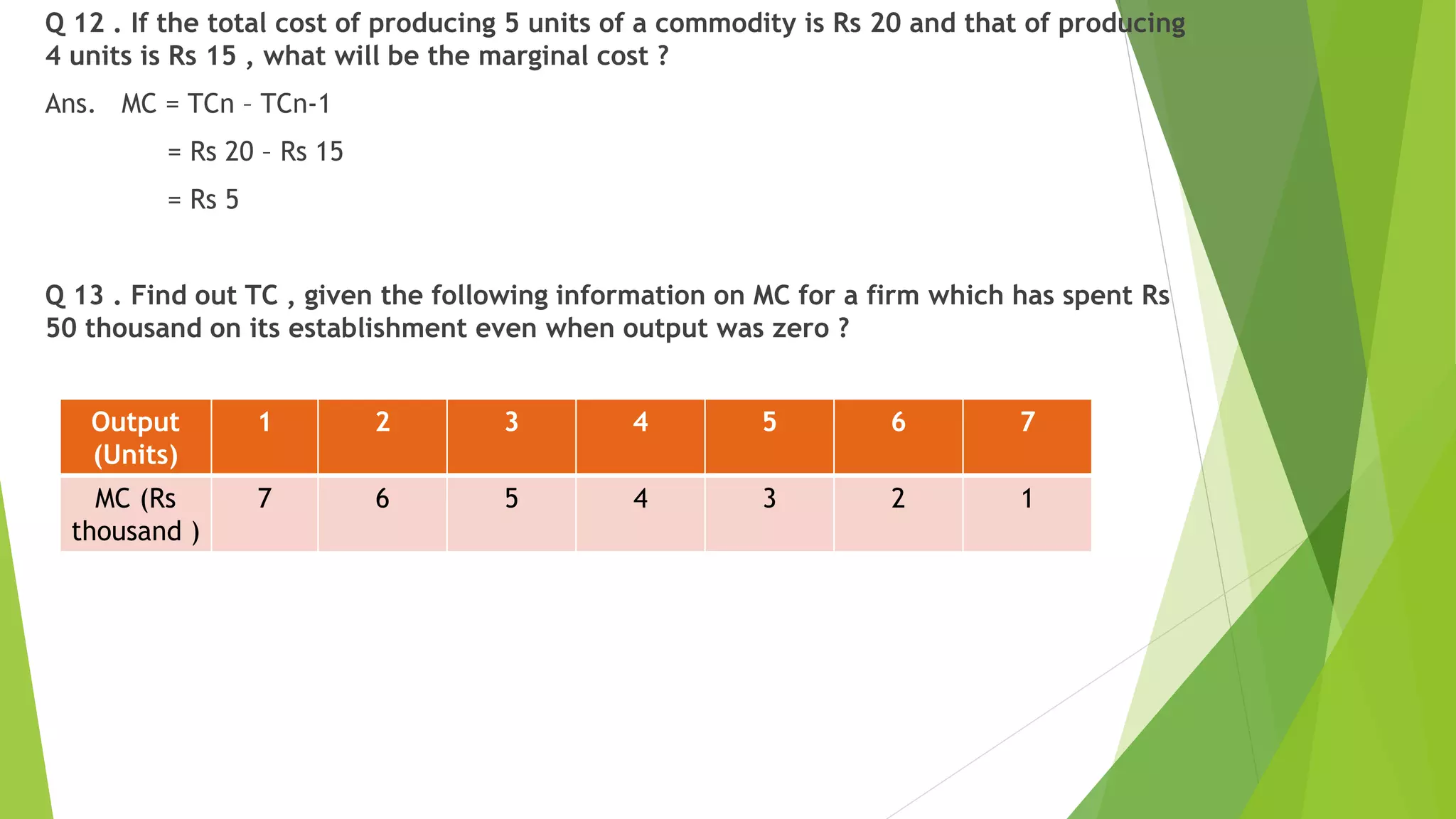
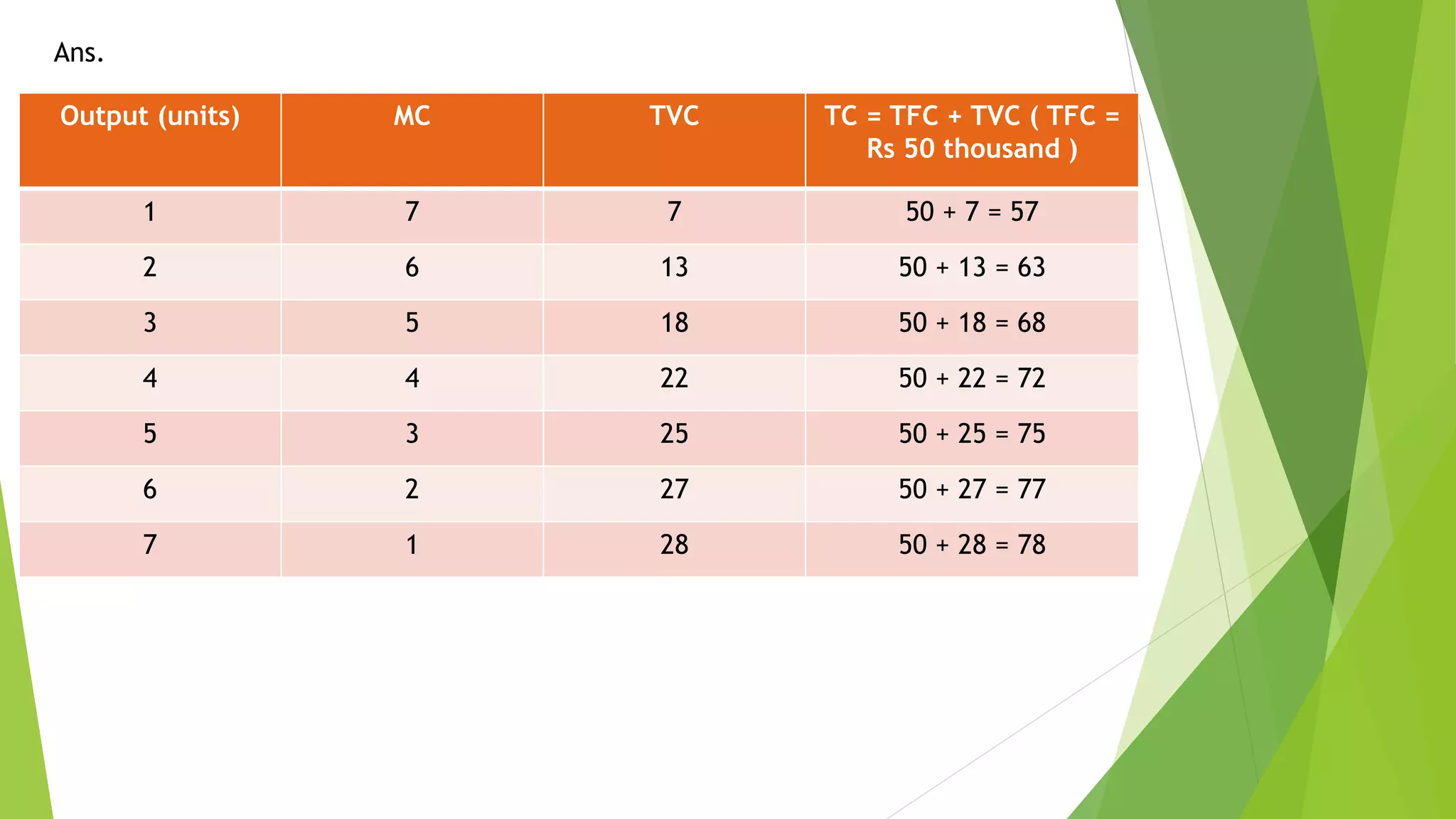
Cost refers to the total expenditure incurred by a producer to produce a given level of output. It includes explicit costs, which are cash payments to factors of production, and implicit costs, which are imputed costs of self-owned resources. Total cost is the sum of fixed costs, which do not vary with output, and variable costs, which do vary with output. Marginal cost is the change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output. It is U-shaped, initially decreasing and then increasing, reflecting the law of variable proportions. Average cost is total cost divided by output and is the sum of average fixed cost and average variable cost.