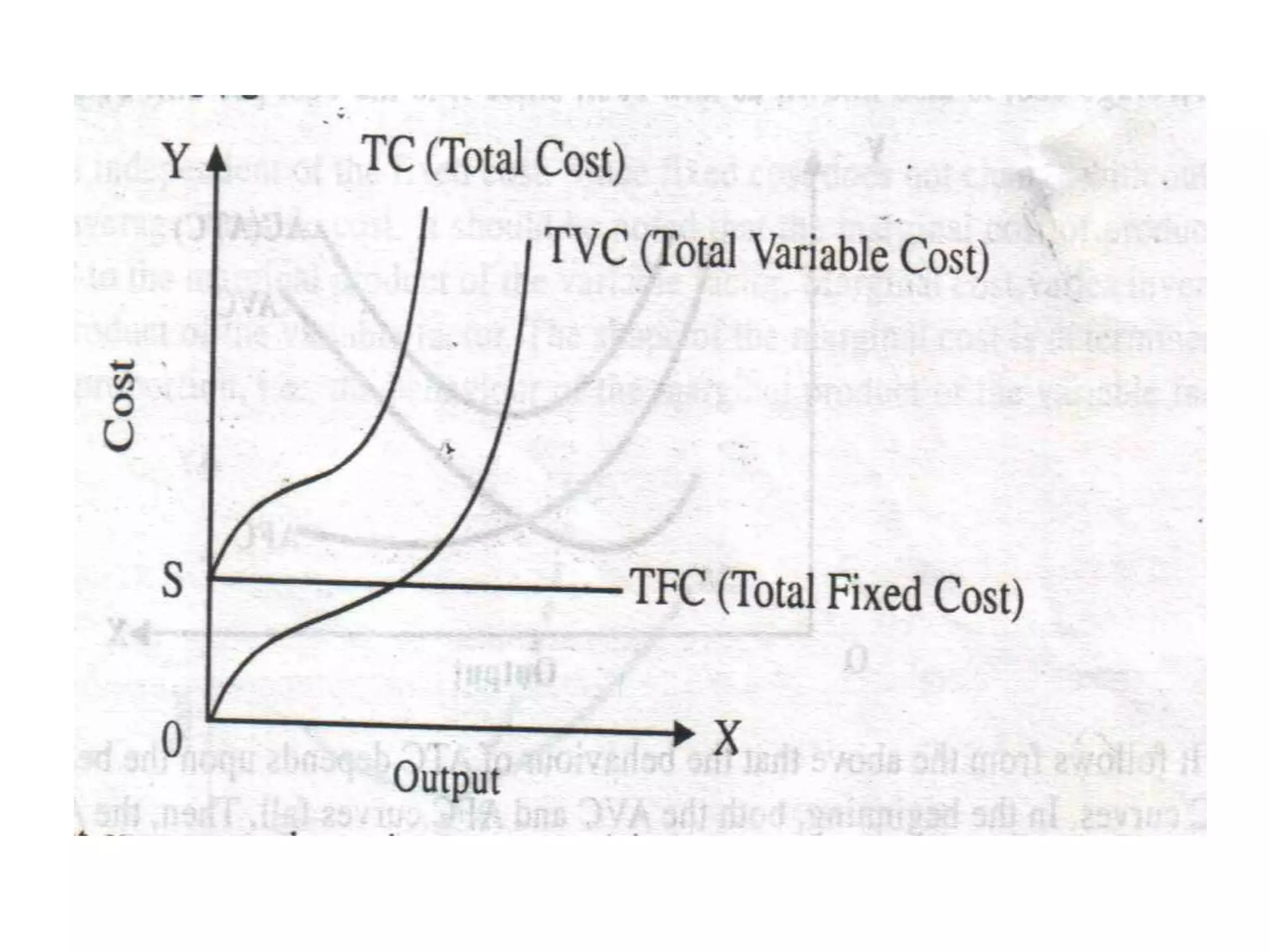
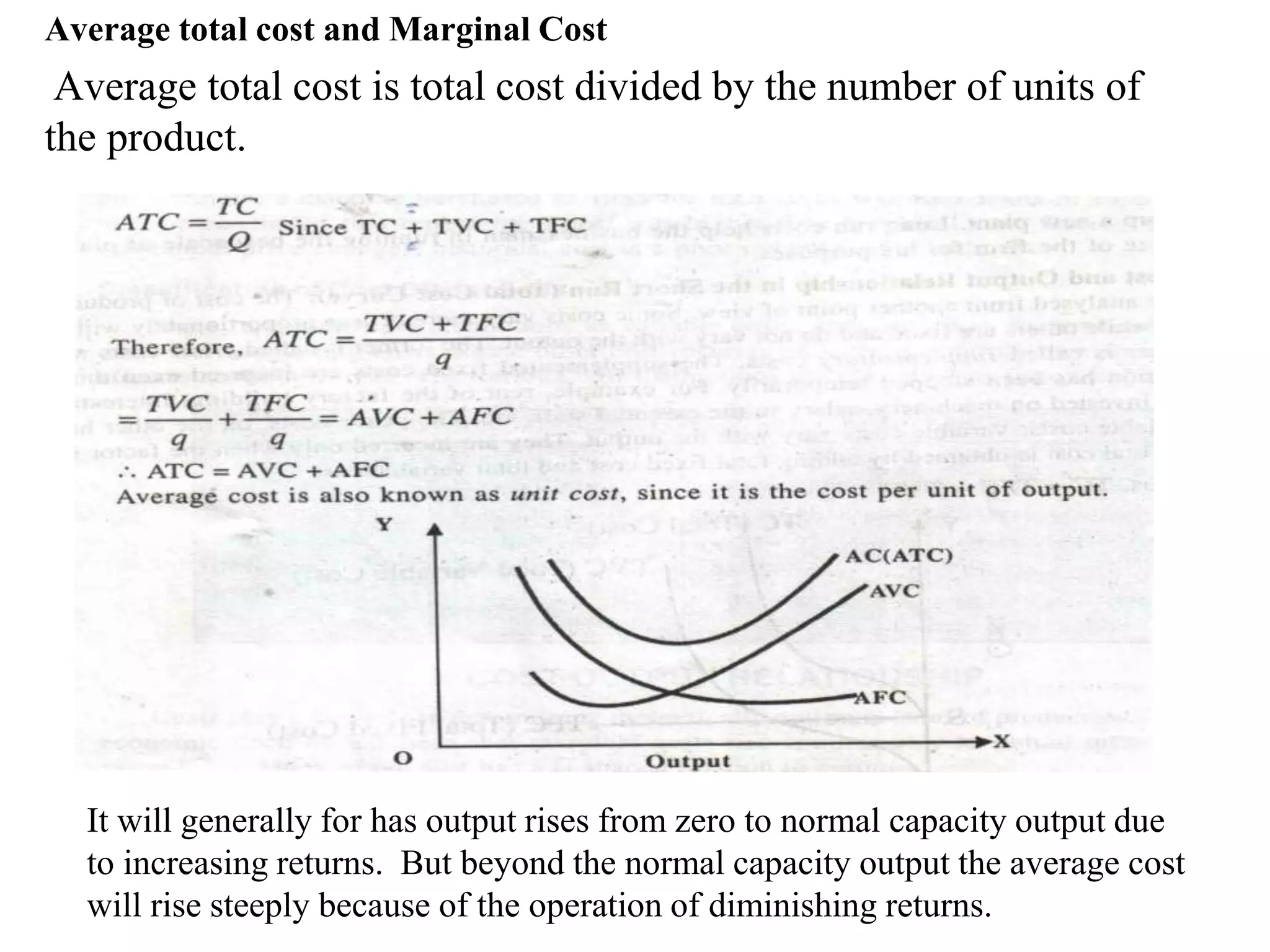
1. Cost is the expense incurred in producing a commodity and is determined by factor input prices. It is the most important factor governing a product's supply.
2. There are different types of costs including explicit costs like wages, implicit costs which do not appear in accounting records, actual costs involving financial expenditures, and opportunity costs which represent the next best alternative use of resources.
3. Cost analysis examines concepts like fixed and variable costs, average and marginal costs, and short-run versus long-run costs to help managers make optimal production decisions.