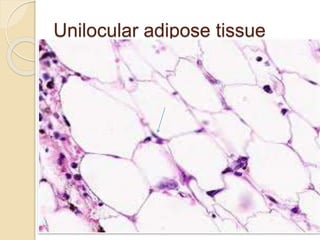
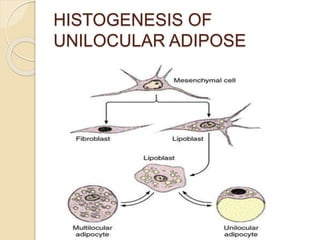
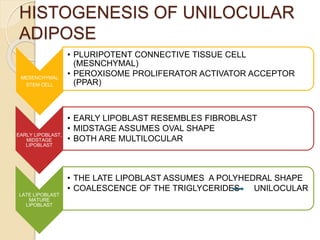
The document discusses unilocular adipose tissue, which is made up of adipocytes containing a single large fat droplet. It is predominantly found in adult humans. Unilocular adipocytes are generally large, spherical cells that have a thin rim of cytoplasm surrounding a large lipid mass. White adipose tissue has important functions such as storing lipids, insulating the body, cushioning organs, and secreting hormones like leptin that regulate appetite and metabolism. The tissue develops from mesenchymal stem cells that differentiate into early and midstage multilocular lipoblasts before maturing into unilocular adipocytes.