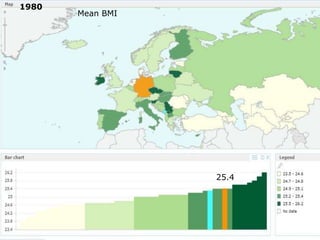
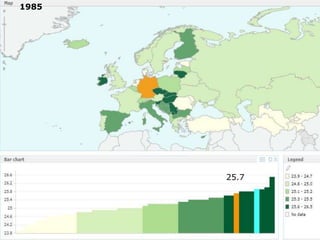
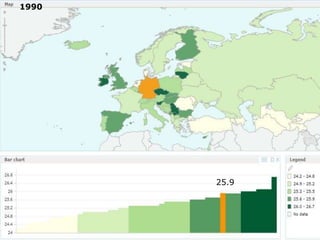
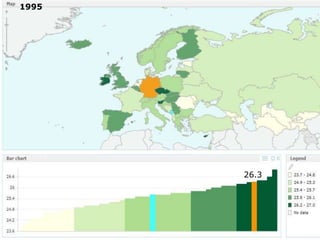
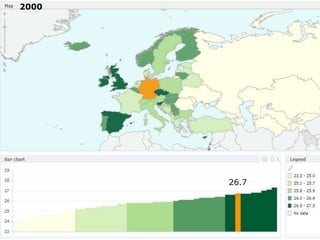
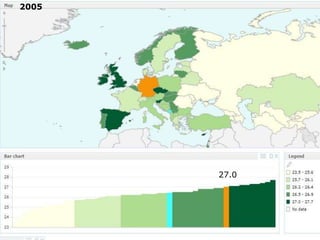
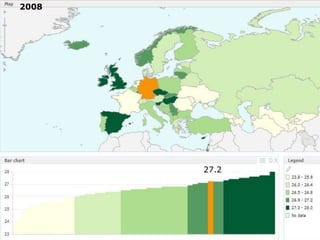
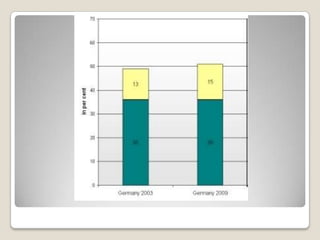
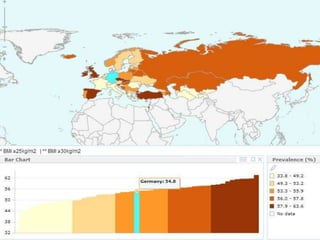
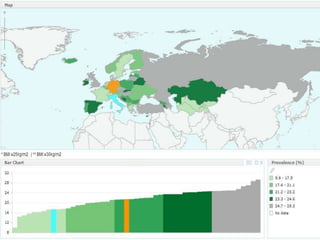
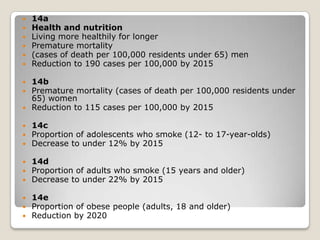
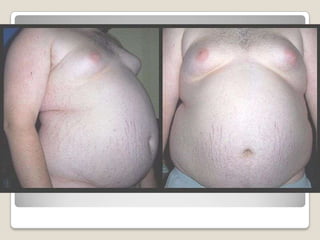
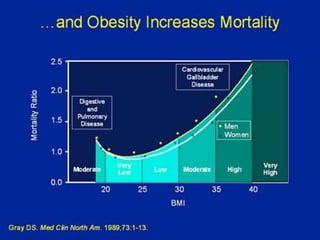
The document discusses obesity in Germany. It notes that over half of Germans are overweight and about 1 in 6 are obese. Obesity rates have doubled since 1980. The German government has launched initiatives to reduce obesity rates by 2020, including education programs on nutrition and exercise in schools, improved food labeling, and limiting junk food marketing to children. Obesity is linked to increased risk of diseases like diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. The health and economic impacts of obesity in Germany are substantial.