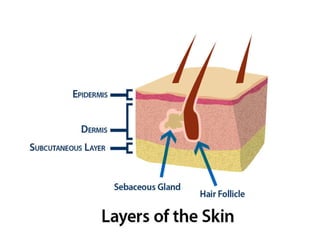
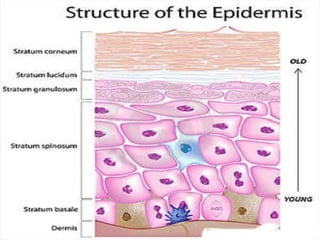
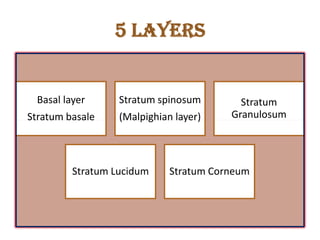
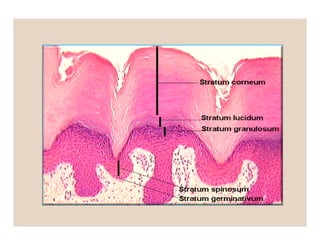
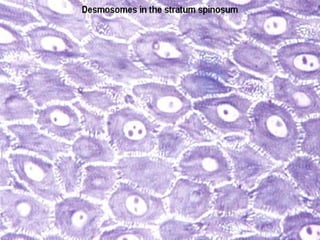
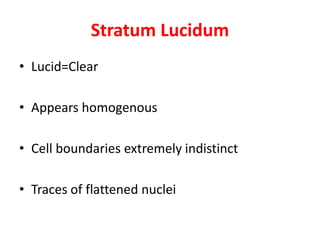
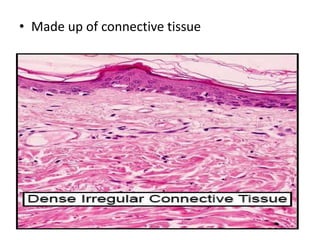
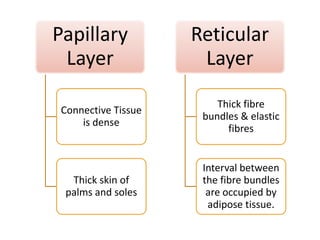
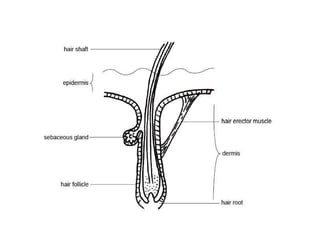
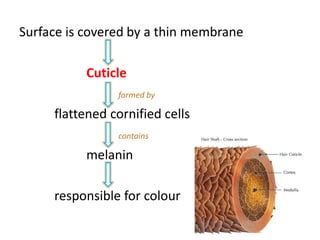
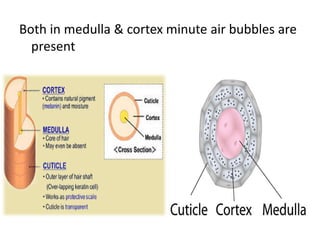
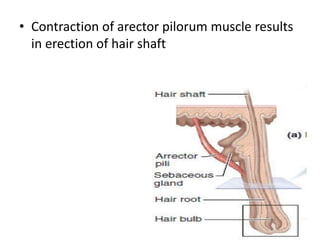
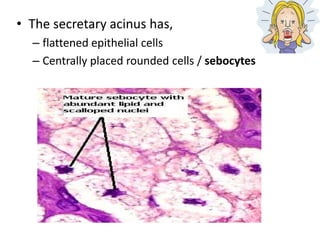
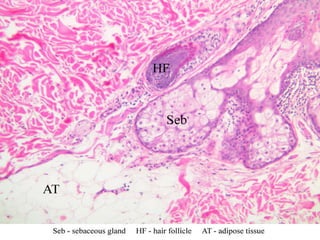
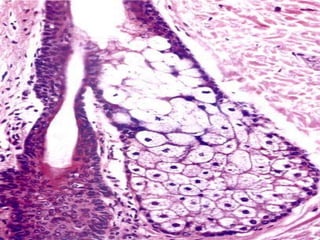
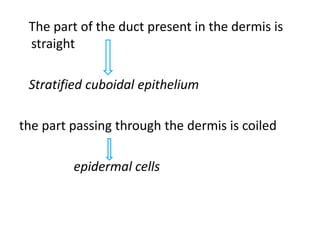
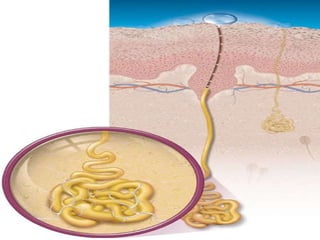
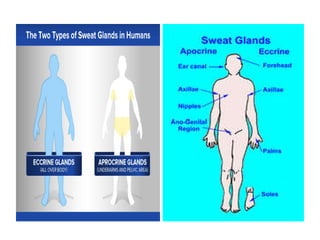
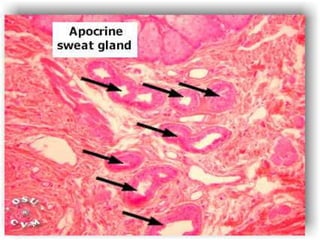
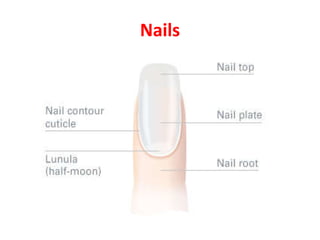
The document summarizes the structure and layers of skin. It describes the three main layers of skin - the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer. It provides details on the 5 layers of the epidermis including the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. It also discusses structures like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails.