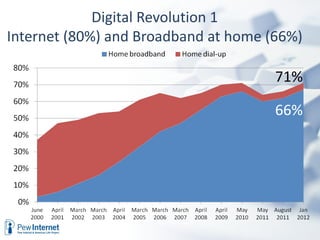
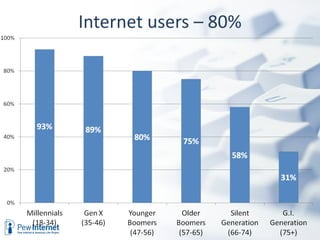
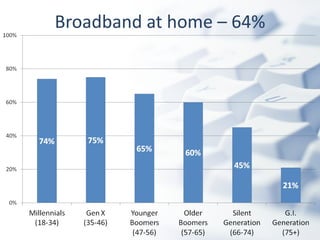
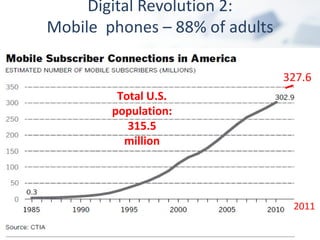
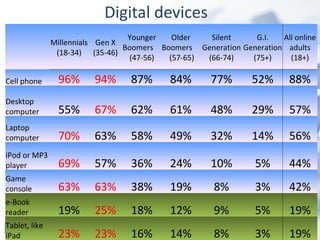
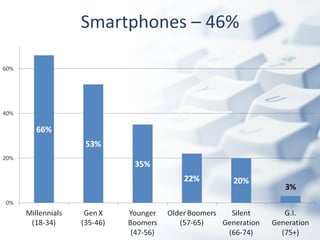
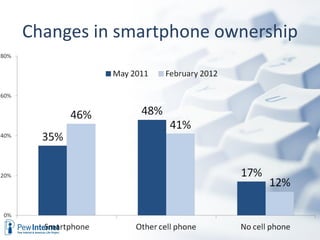
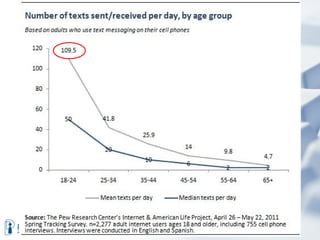
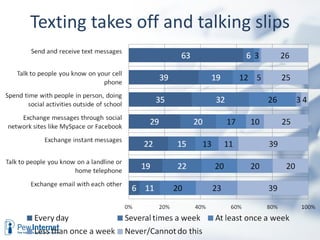
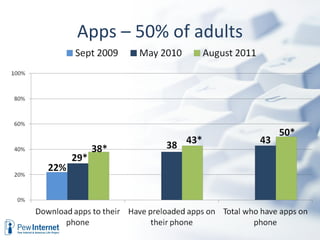
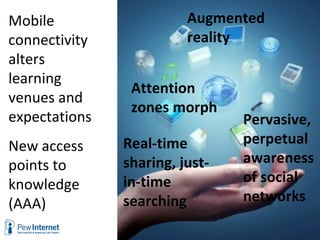
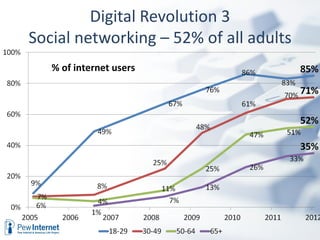
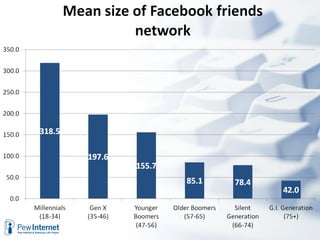
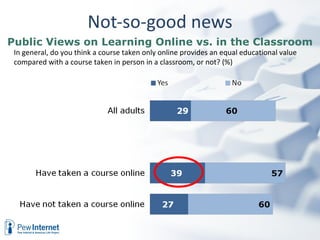
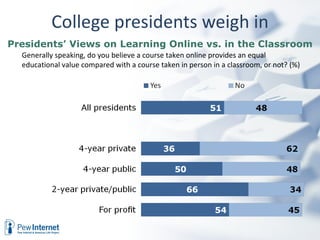
The document discusses how digital technologies and the internet are shifting the landscape of learning. Broadband facilitates networked learning through links and multimedia. Social media aids peer-to-peer learning as people share content and expertise online. Mobile connectivity alters learning venues and expectations as people access information anywhere through their phones. These changes are giving rise to new kinds of learners who are more self-directed, collaborative, and oriented towards producing knowledge.