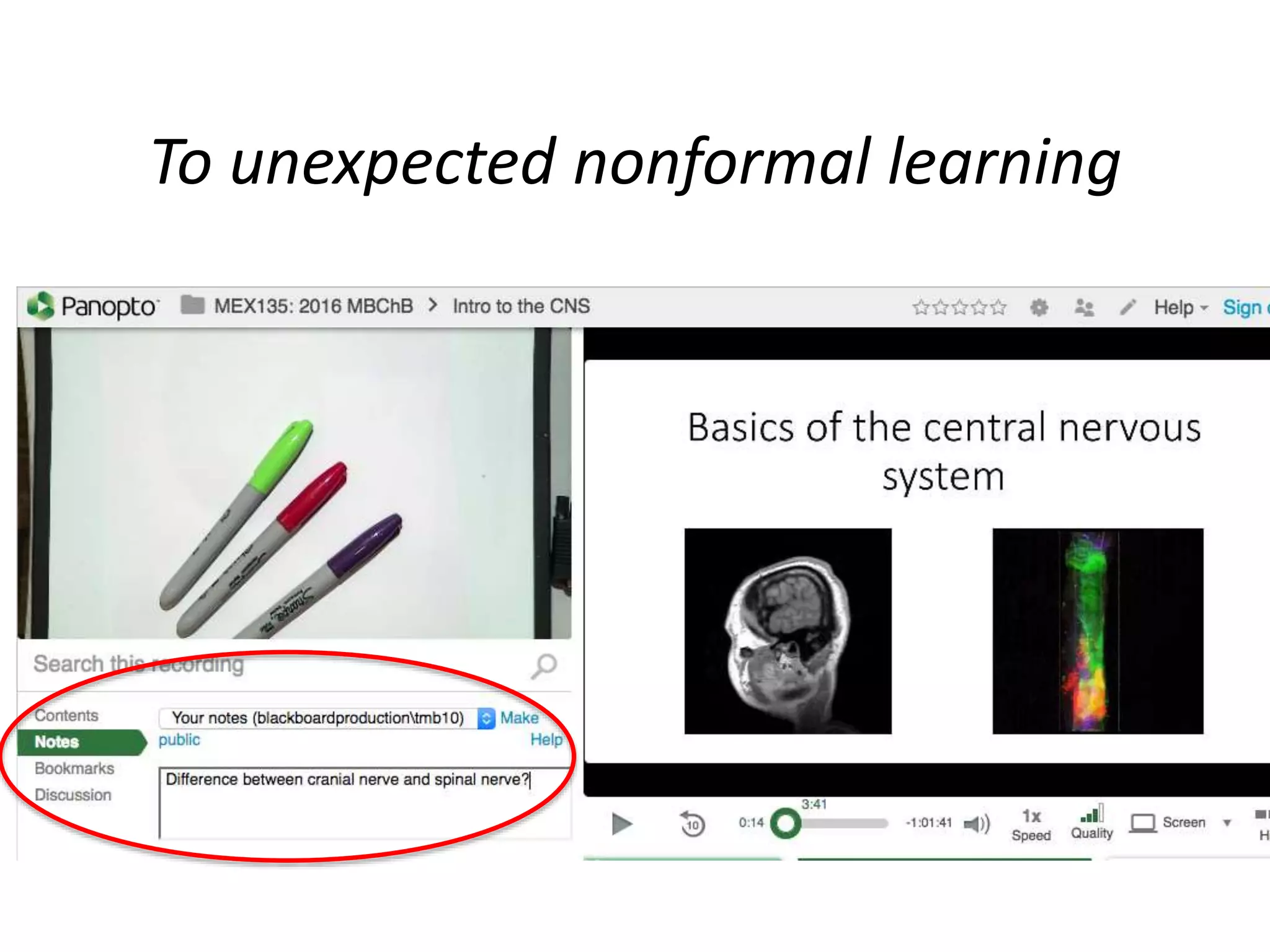
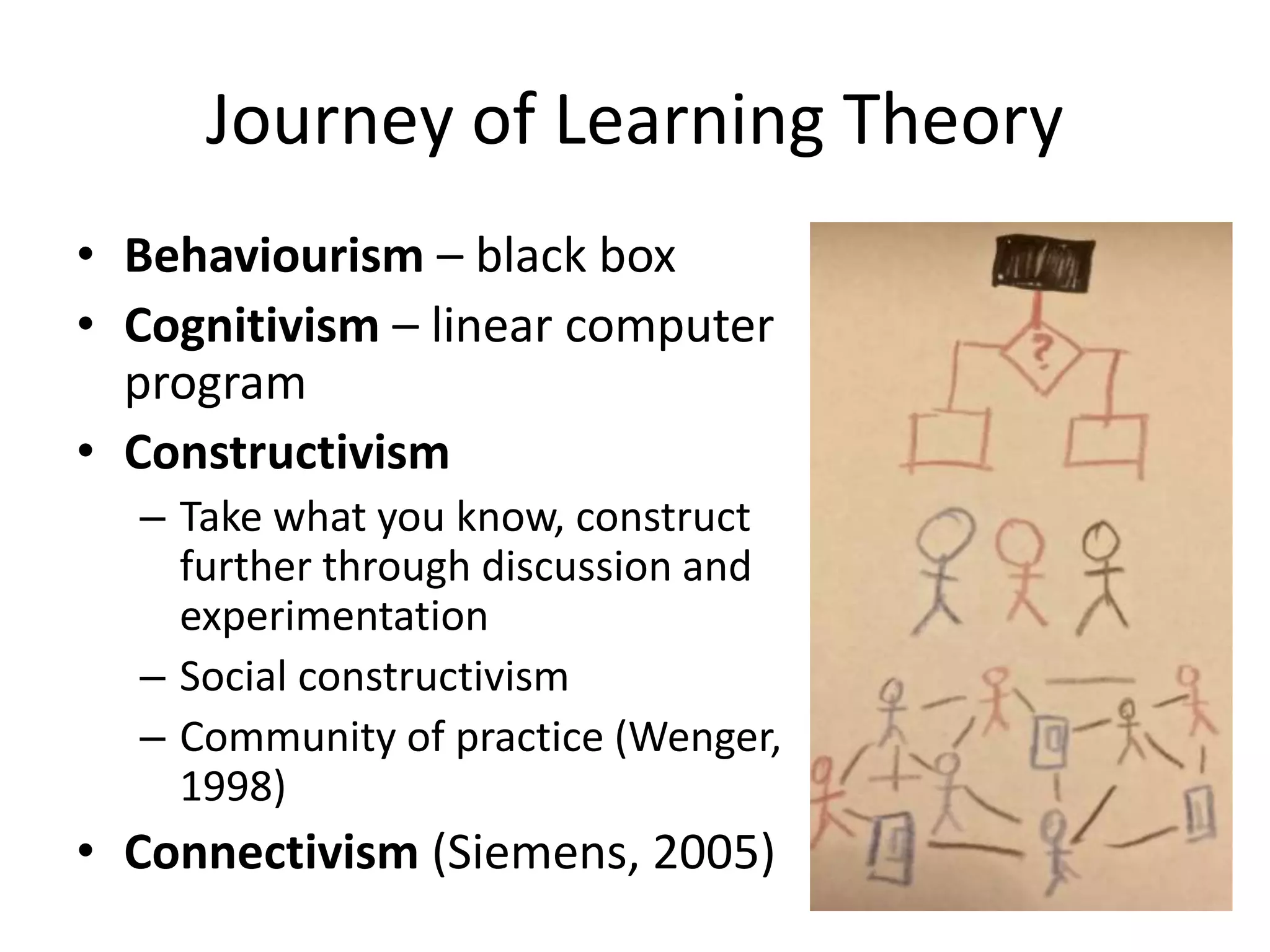
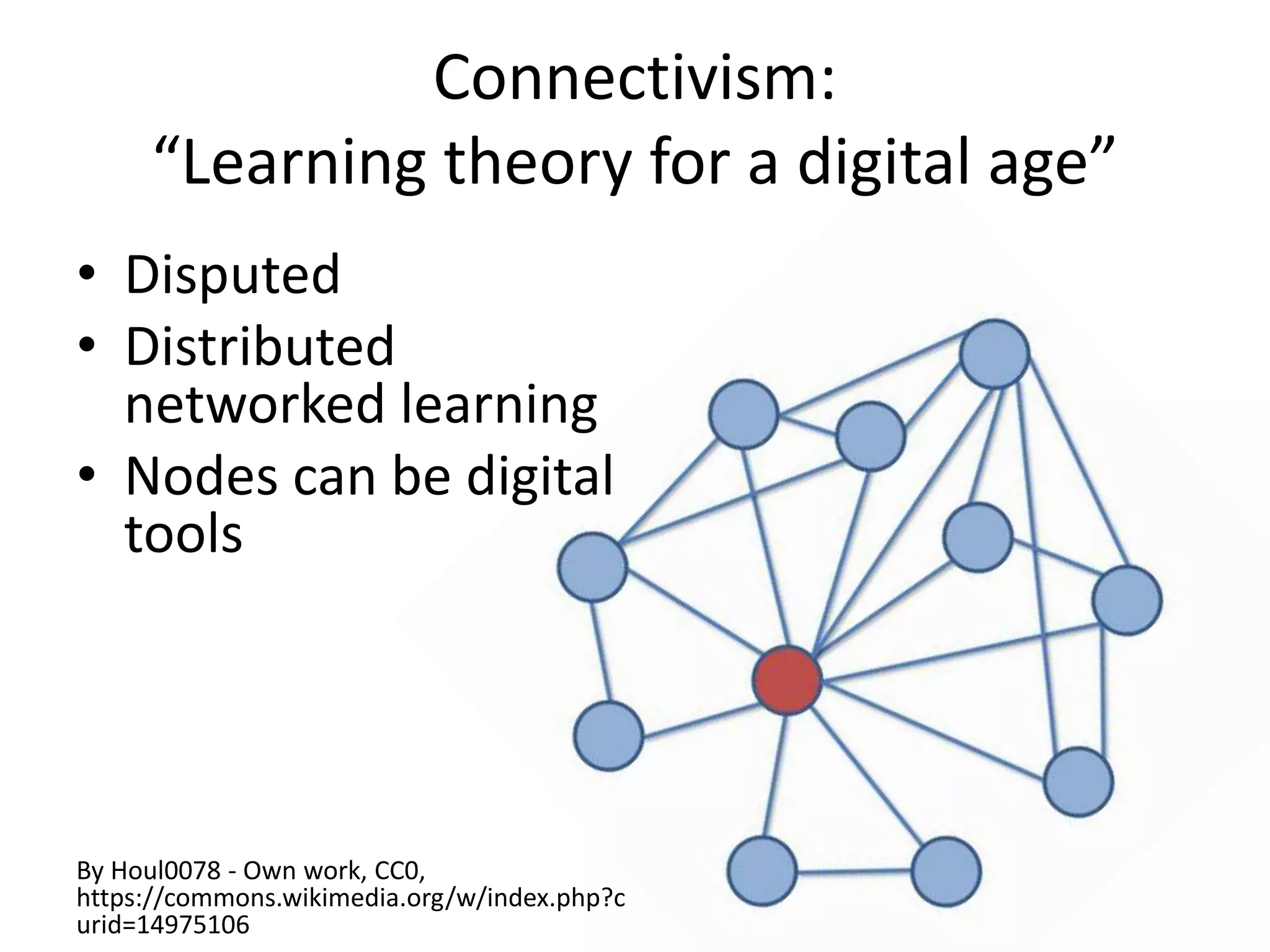
The presentation discusses the complexities of digital learning, emphasizing the distinctions between formal, informal, and nonformal learning. It highlights emerging concepts like rhizomatic learning and connectivism as alternatives to traditional learning theories, suggesting that digital tools empower students and foster active, student-led experiences. Key takeaways include the necessity for academic understanding of learning technology and the importance of leveraging digital tools to meet the needs of learners.





![Rhizomatic learning (Cormier, 2008)
• A rhizome is a plant with no traditional stem
• By Kenraiz (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA
4.0-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0-3.0-2.5-2.0-
1.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vjbiv79uquqxi2vwerqm-signature-44f7b0de1201eed0f6fe8dc7013a11b8f9c7e8273ca6a5942a376c96aa62a948-poli-171121150743/75/The-Digital-Learning-Journey-Going-in-Expected-and-Unexpected-Directions-8-2048.jpg)






![Subversive Learning
• Learning material not originating from the
course author
• Students do what they think they must do
• Cautionary tales
By Hariadhi, myself (Own work) CC BY 2.5
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)], via](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vjbiv79uquqxi2vwerqm-signature-44f7b0de1201eed0f6fe8dc7013a11b8f9c7e8273ca6a5942a376c96aa62a948-poli-171121150743/75/The-Digital-Learning-Journey-Going-in-Expected-and-Unexpected-Directions-21-2048.jpg)







![References
• Bogue, R. (2008) Deleuze and Guattari, Routledge.
• Cormier, D. (2008) ‘Rhizomatic Education: Community as Curriculum’,
Innovate: Journal of Online Education, 4(5), p. 6, [online] Available from:
http://nsuworks.nova.edu/innovate%5Cnhttp://nsuworks.nova.edu/innov
ate/vol4/iss5/2.
• Genosko, G. (2001) Deleuze and Guattari, Taylor & Francis (ed.).
• Lockspeiser, T. M., O’Sullivan, P., Teherani, A. and Muller, J. (2008)
‘Understanding the experience of being taught by peers: the value of
social and cognitive congruence’, Advances in Health Sciences Education,
13(3), pp. 361–372, [online] Available from:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17124627 (Accessed 31 December
2016).
• Siemens, G. (2005) ‘Connectivism: A learning theory for the Digital Age’,
International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning, 2,
pp. 1–8, [online] Available from:
http://www.itdl.org/Journal/Jan_05/article01.htm.
• Wenger, E. (1998) ‘Communities of Practice: Learning, Meaning, and
Identity’, Systems thinker, 9, pp. 2–3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vjbiv79uquqxi2vwerqm-signature-44f7b0de1201eed0f6fe8dc7013a11b8f9c7e8273ca6a5942a376c96aa62a948-poli-171121150743/75/The-Digital-Learning-Journey-Going-in-Expected-and-Unexpected-Directions-32-2048.jpg)