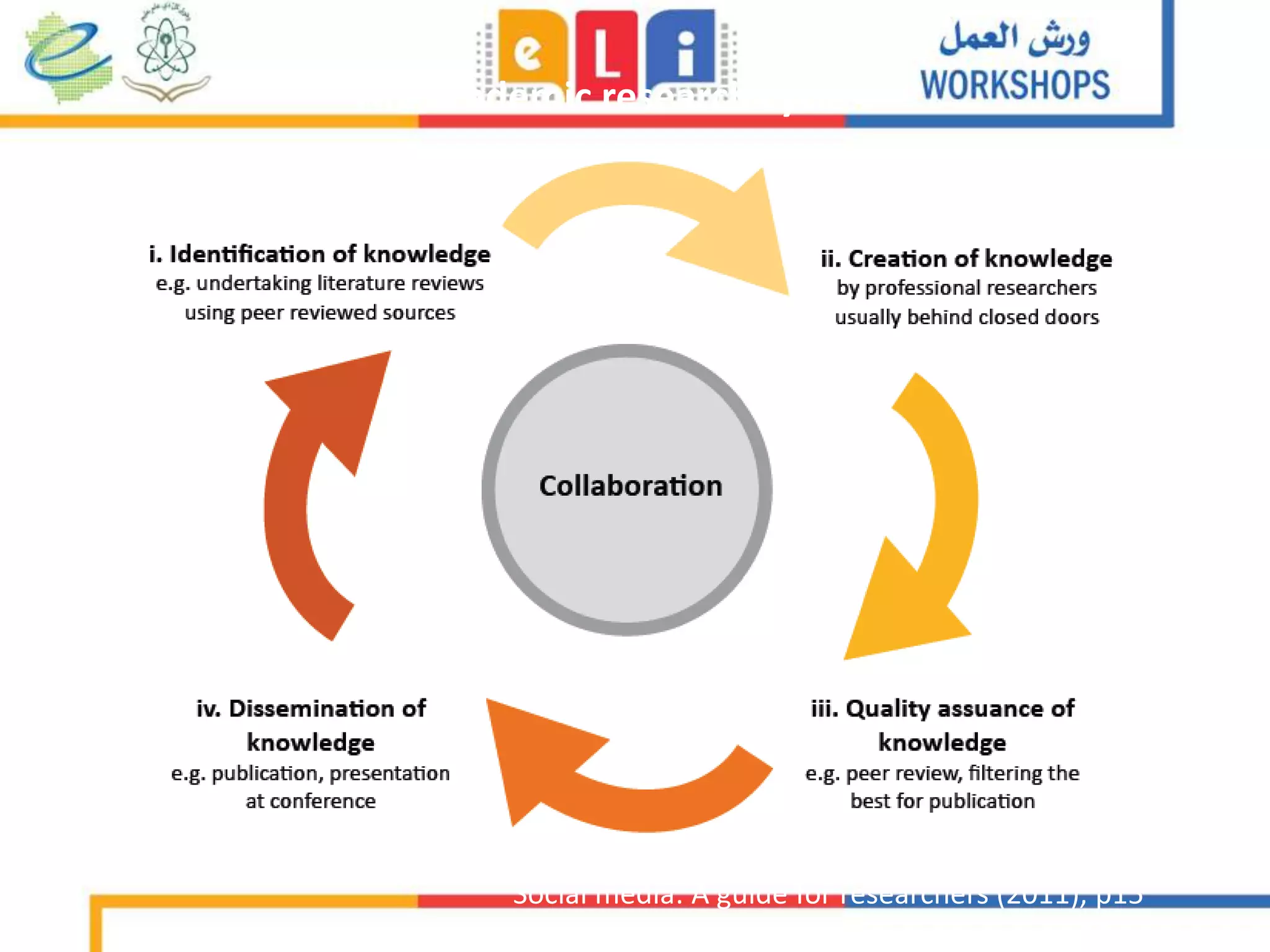
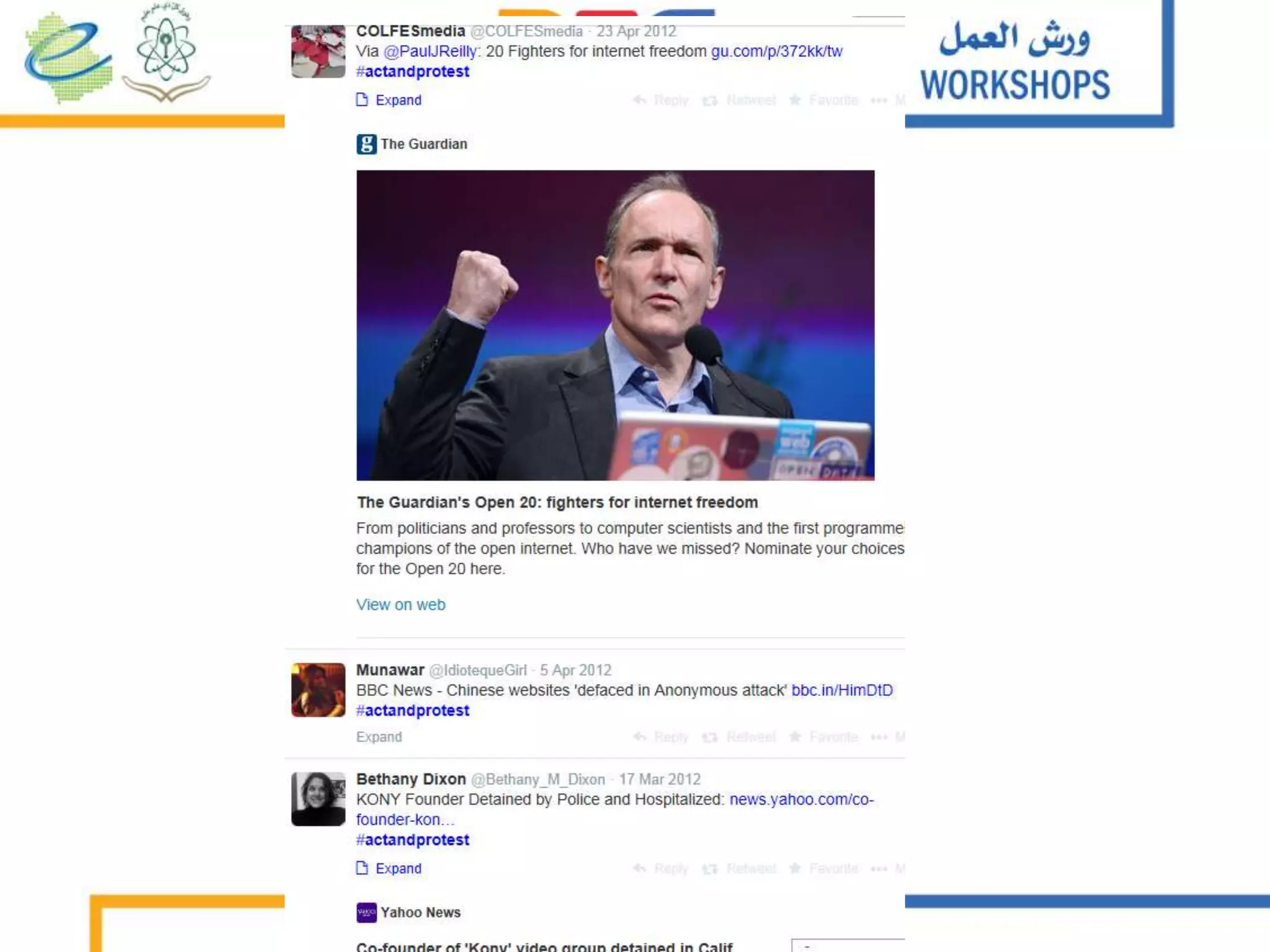
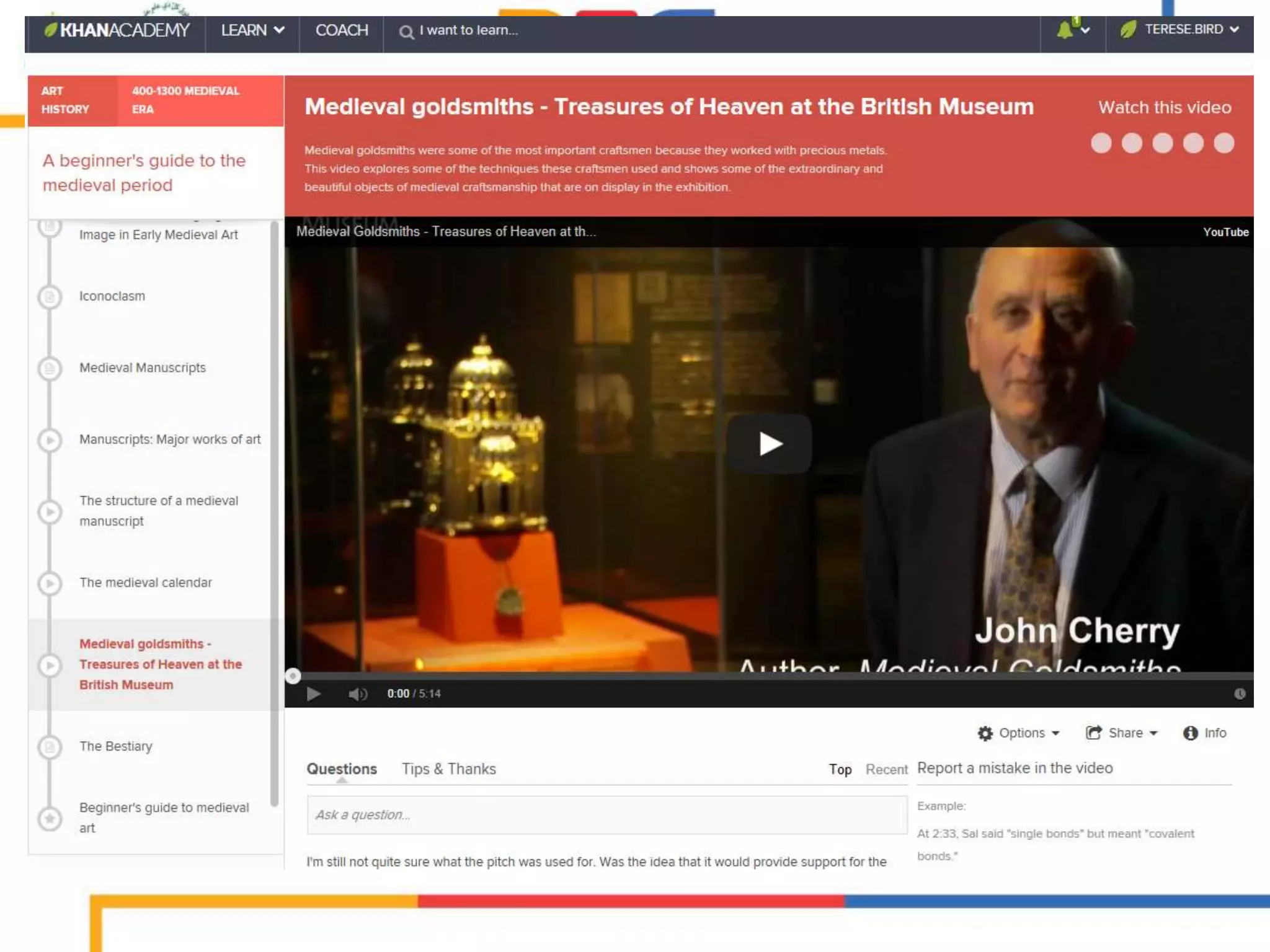
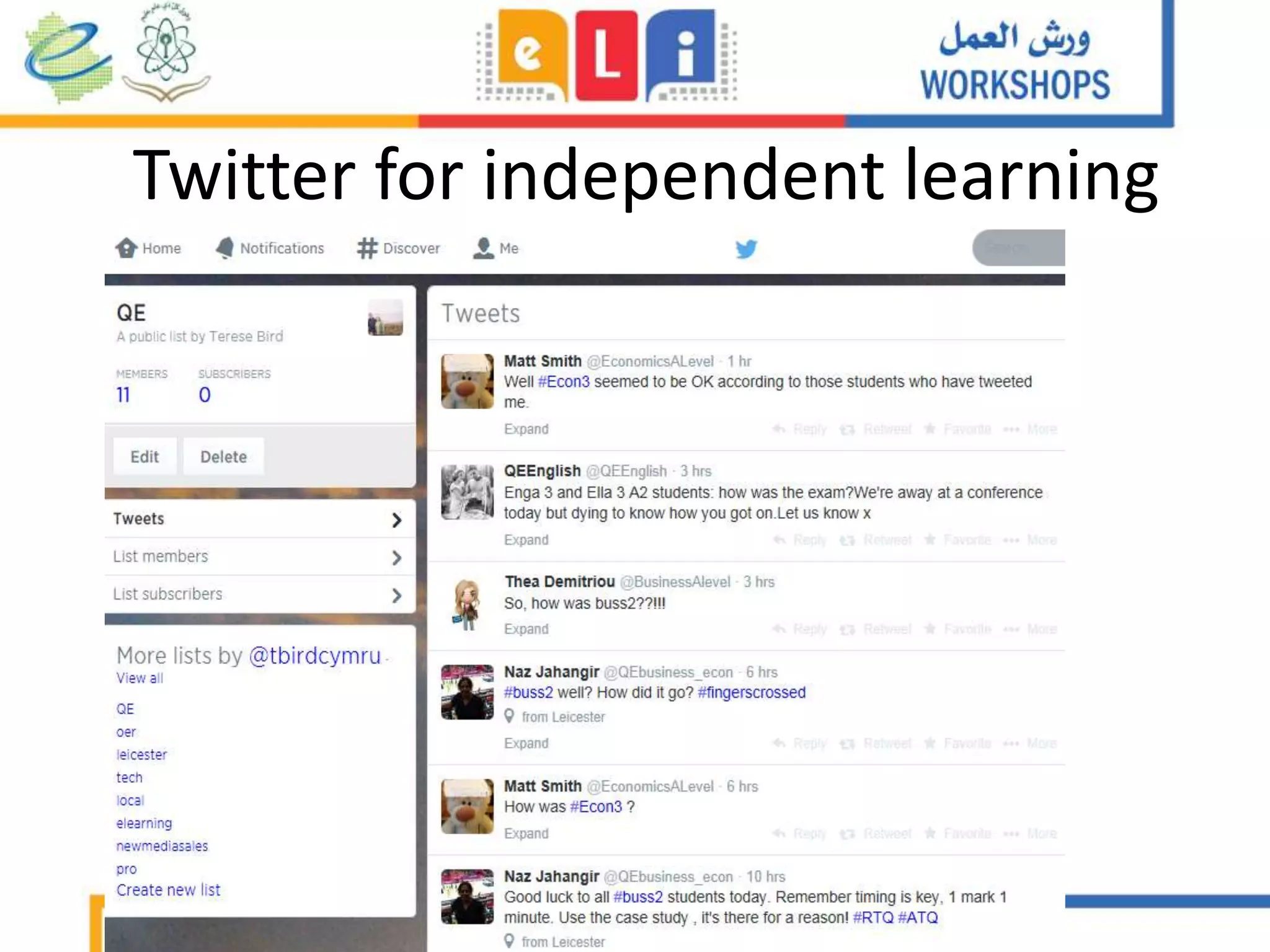
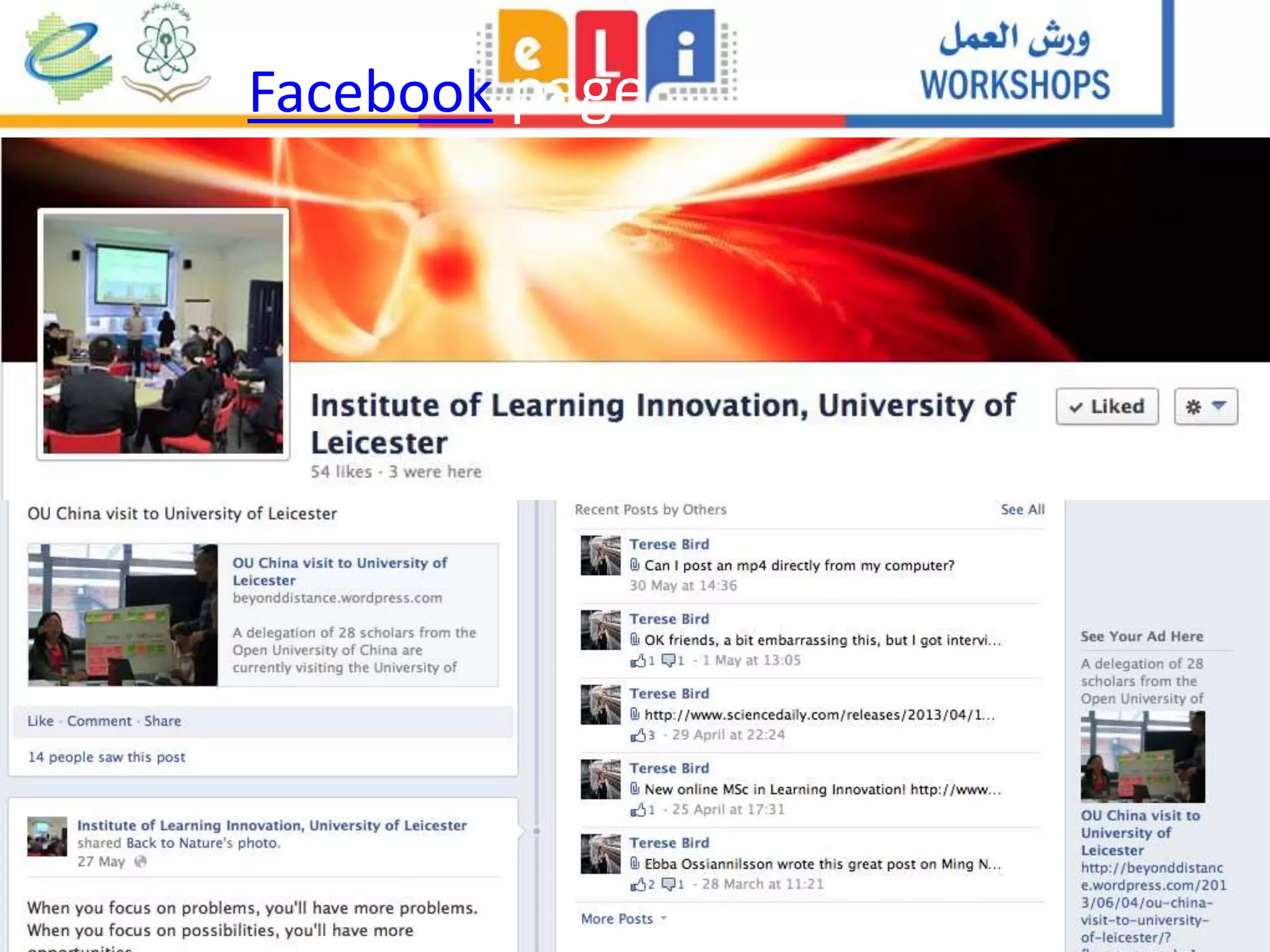
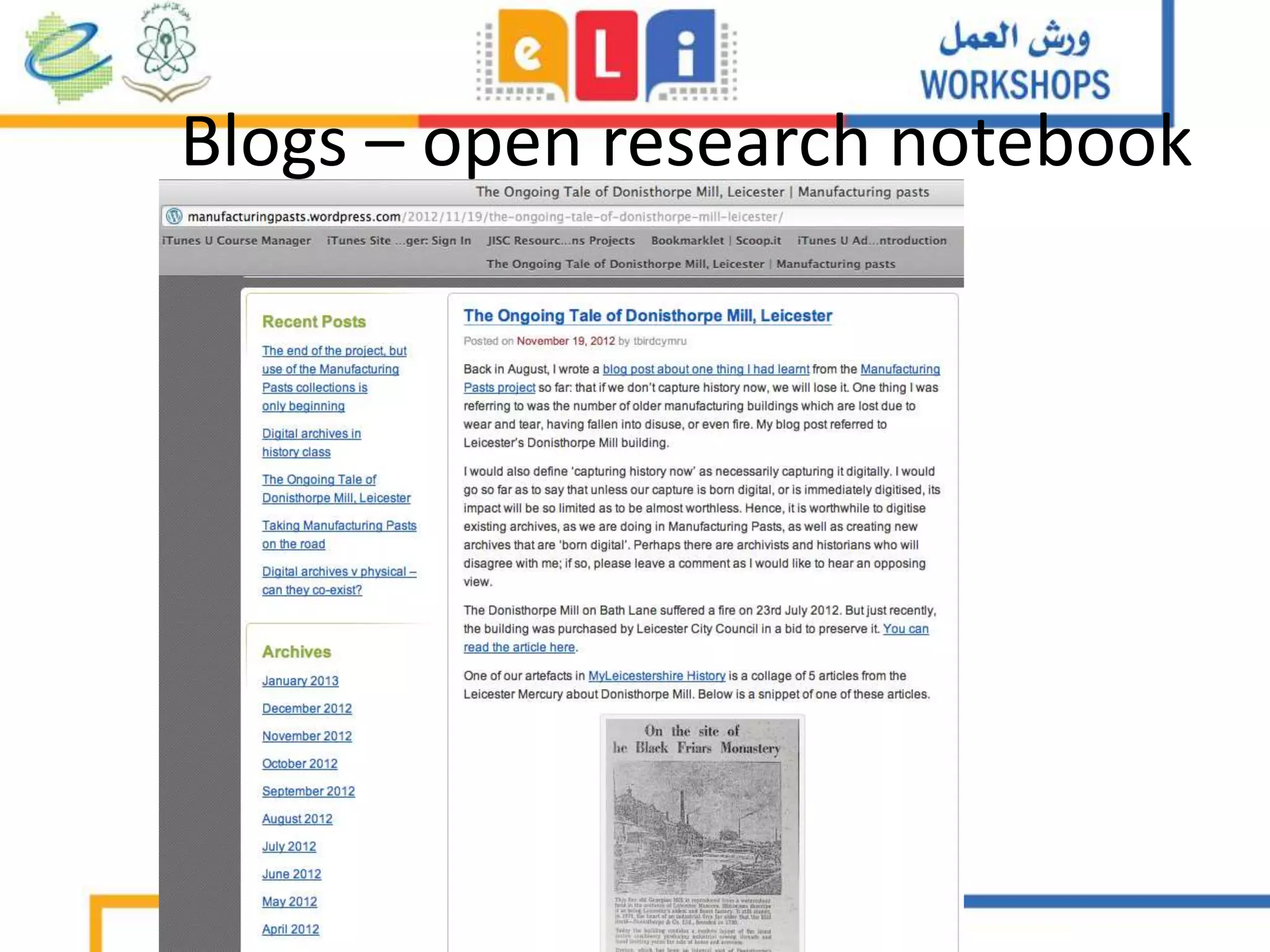
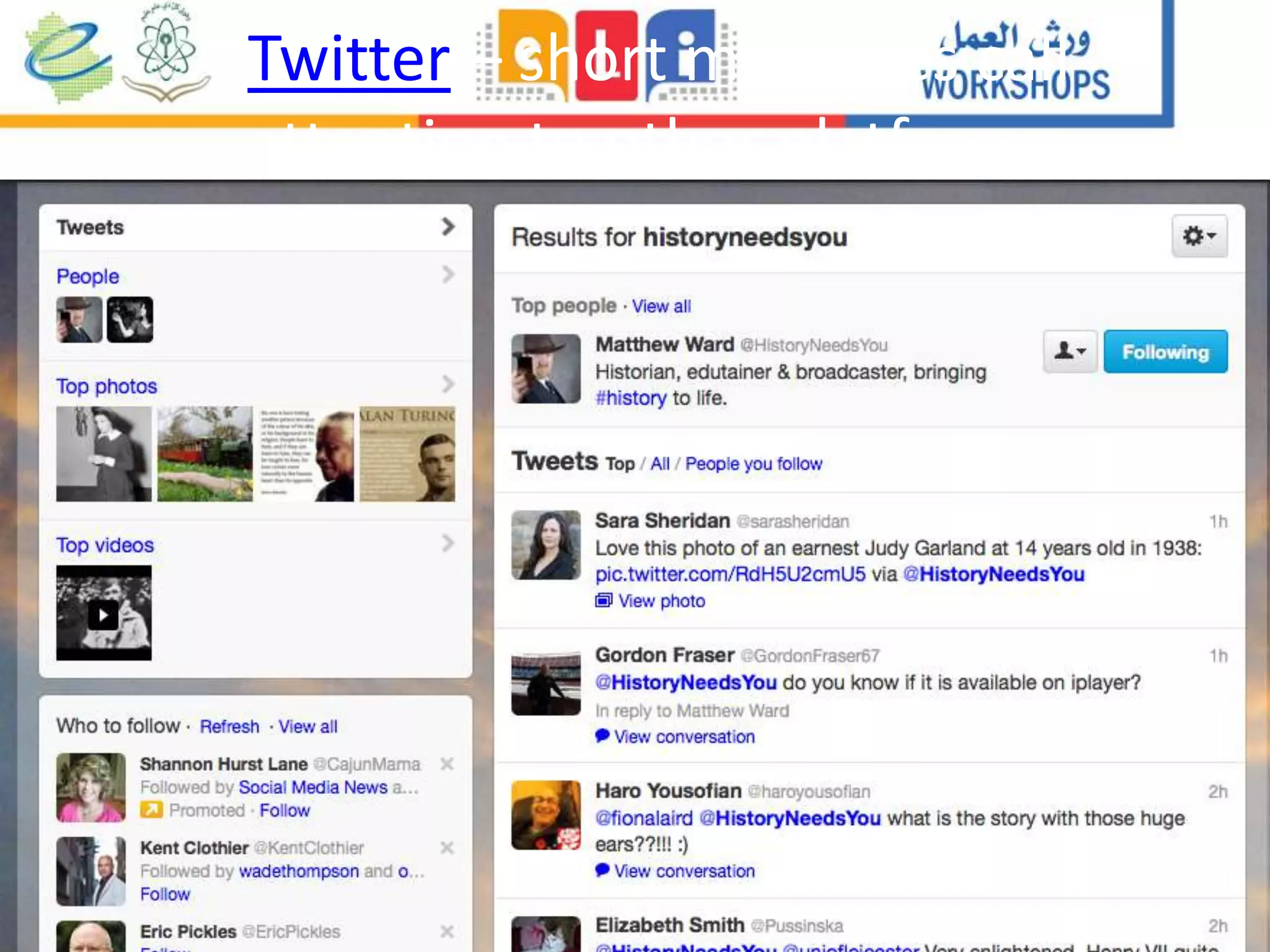
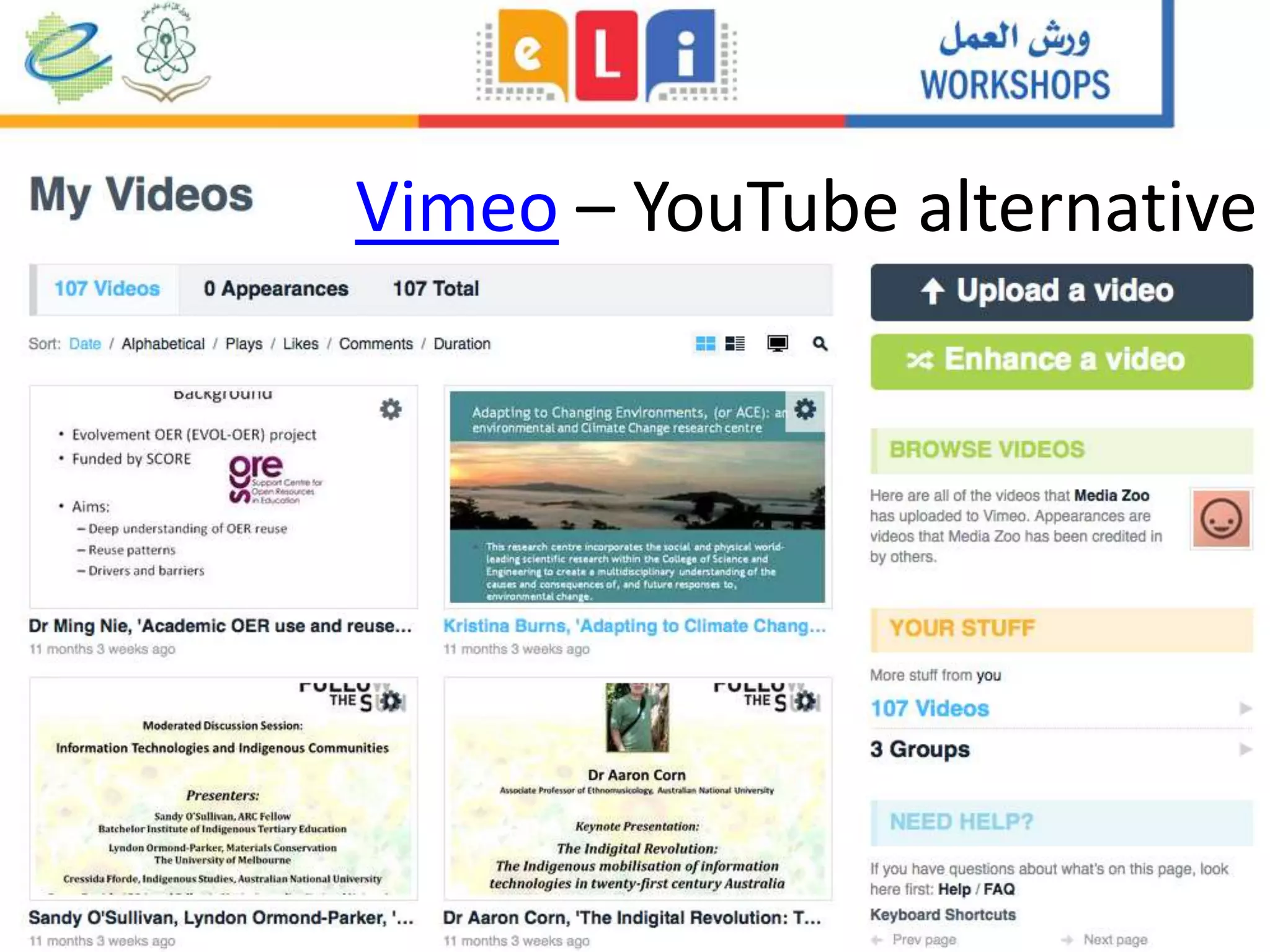
The document discusses the integration of mobile learning management systems and social media tools in academic research and teaching. It highlights effective uses of social media such as Twitter and YouTube for independent learning, the importance of digital literacy, and resources for educators to enhance students' learning experiences. Additionally, it examines the evolving landscape of digital skills required in academia and the workplace.