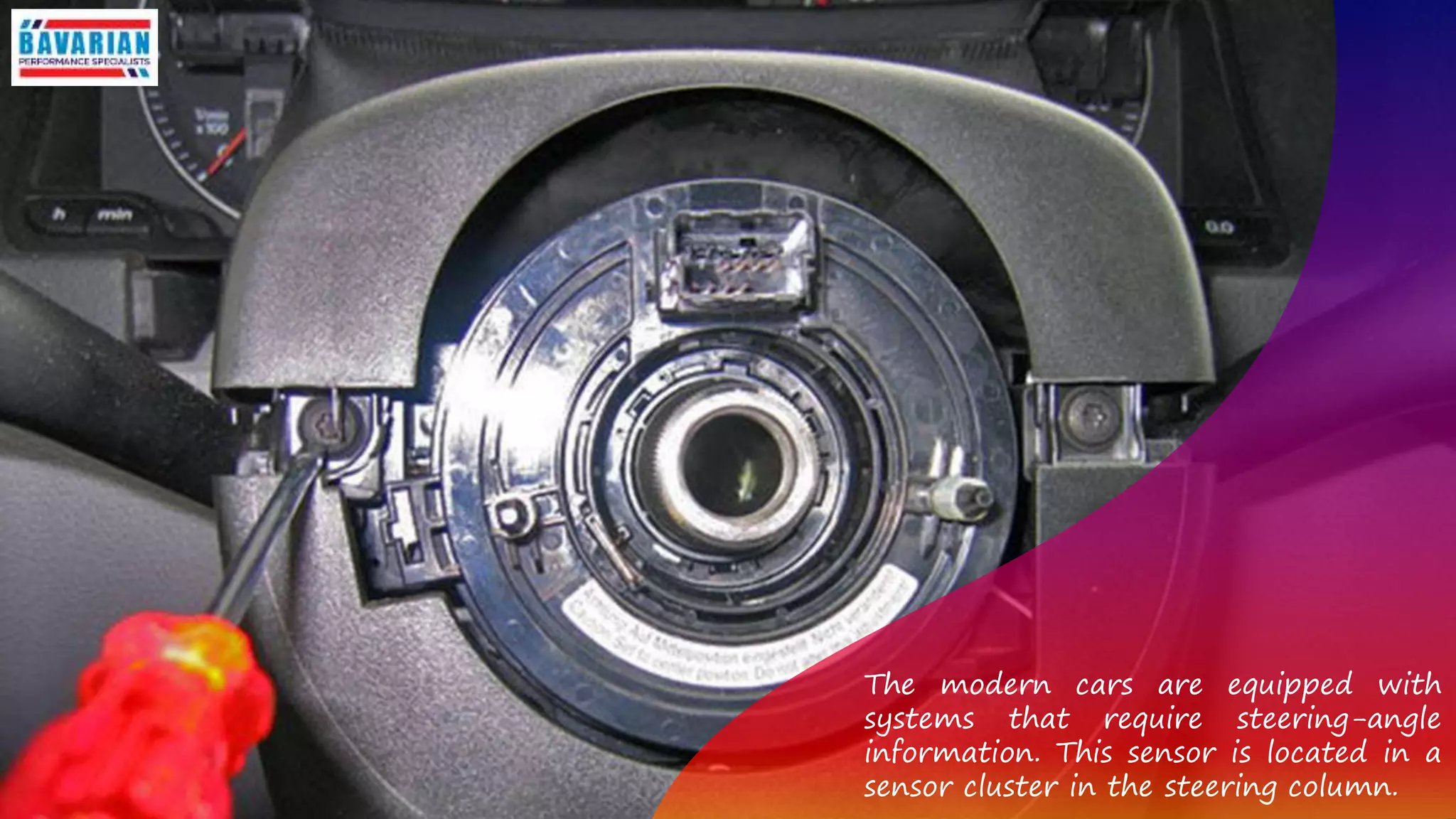
The steering angle sensor is a crucial component in a car's electronic control system that measures the steering wheel's position and rate of turn. It provides accurate angle information immediately after ignition and communicates this data via a controller area network interface, ensuring safety through internal plausibility checks and diagnostics. The sensor utilizes unique measuring principles to track steering dynamics and is often packaged with multiple sensors for redundancy and improved accuracy.