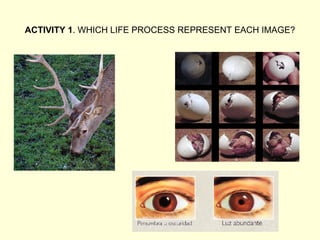
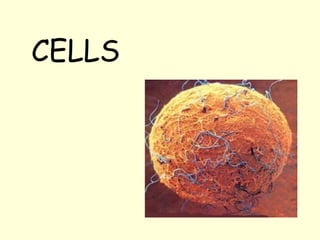
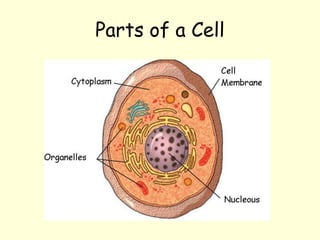
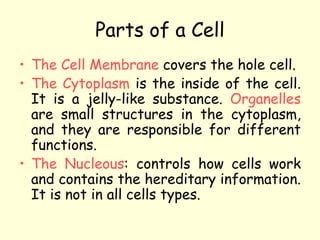
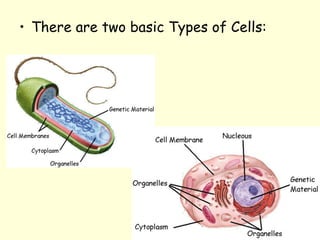
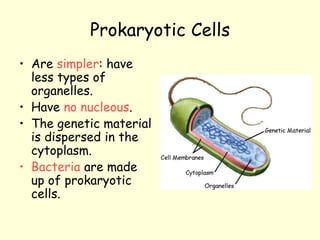
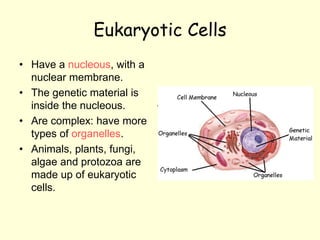
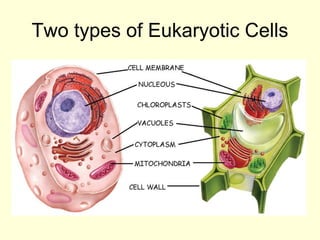
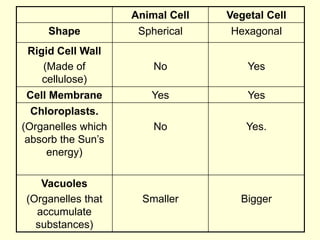
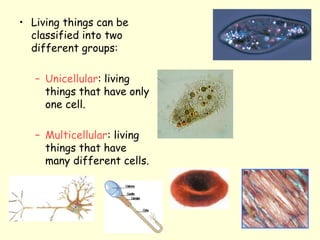
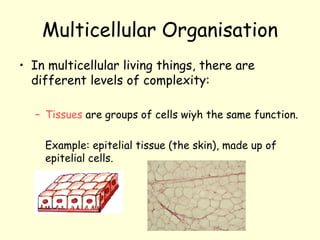
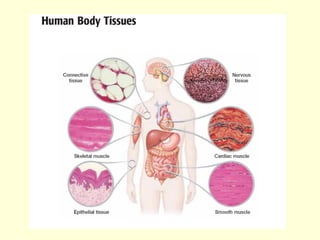
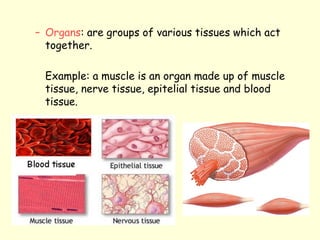
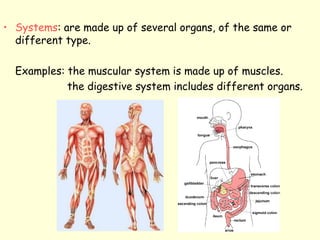
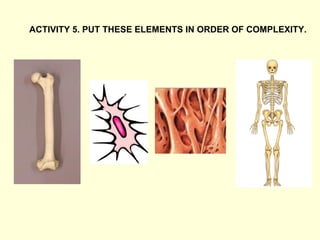
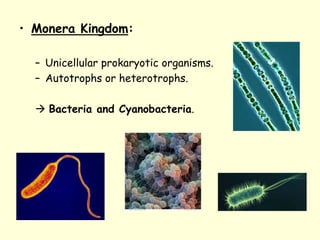
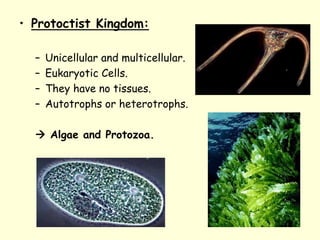
The document summarizes key concepts about life processes, cells, and classification of living things. It outlines that all living things share three main life processes: nutrition, reproduction, and interaction with the environment. It then describes the basic unit of life - the cell, and explains the main parts of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Finally, it introduces the five-kingdom classification system used to categorize living things based on cell structure and nutrition.