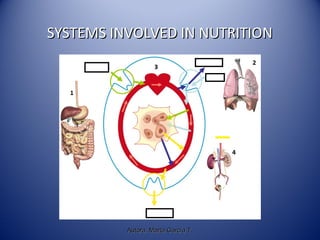
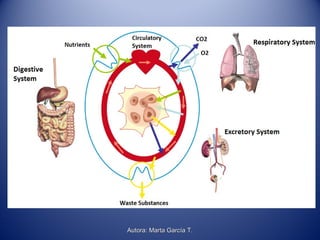
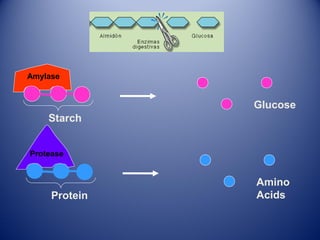
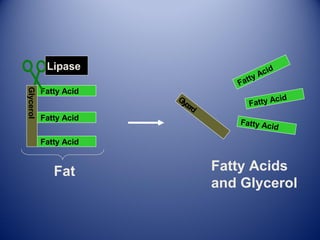
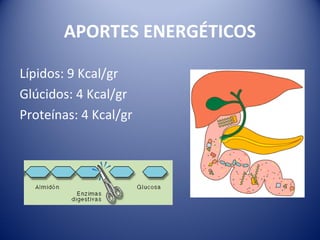
This document discusses human nutrition and the systems involved. It defines nutrition as the processes by which the body obtains nutrients from food and transports them through the body. The digestive, respiratory, circulatory, and excretory systems are involved in nutrition. Nutrients include organic substances like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and vitamins, as well as inorganic minerals and water. A balanced diet provides energy and regulates the body's functions. Special diets and food preservation methods help ensure proper nutrition.