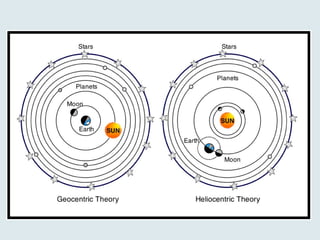
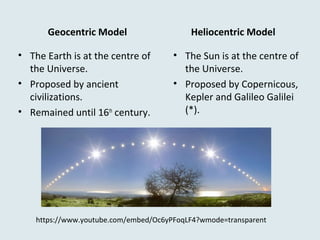
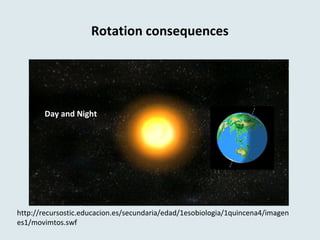
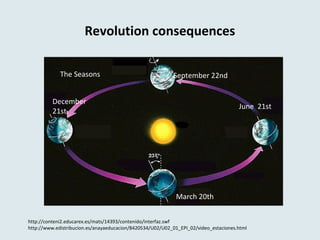
The document describes key features of Earth and its place in the universe. It notes that Earth is a rocky planet with an atmosphere containing oxygen, an average temperature of 15°C, and a water cycle. It orbits the Sun in an elliptical revolution taking 365 days, which causes the seasons, and rotates on its axis in 24 hours causing day and night. The Earth has spheres including the geosphere of crust, mantle and core, hydrosphere of water, atmosphere of air, and biosphere of life. The Moon orbits Earth every 28 days, causing tides, and eclipses can occur when the Moon blocks the Sun or Earth blocks the Sun.