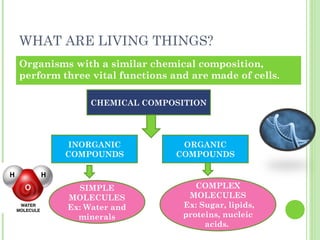
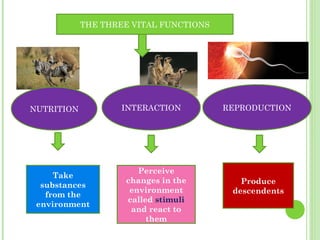
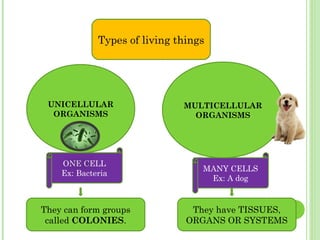
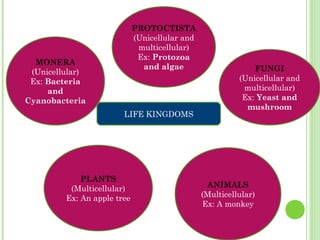
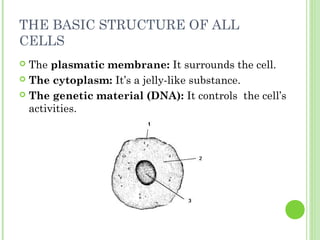
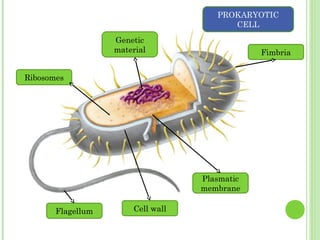
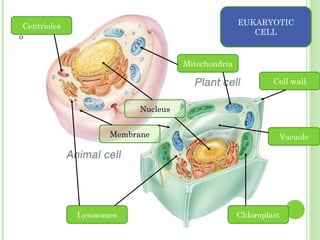
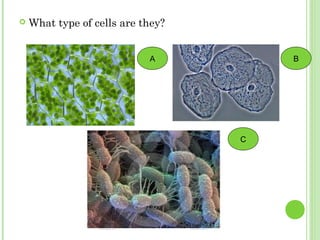
This document provides information on living organisms and cells. It discusses the chemical composition, vital functions, and cellular structure of living things. All living things are made of cells, which are the basic functional units. Cells come in two types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria have no nucleus, while eukaryotic cells found in plants, animals and fungi have membrane-bound nuclei. The document also categorizes different types of multicellular organisms based on their levels of cellular organization.