1) Living organisms have key characteristics of nutrition, interrelation with their environment, and reproduction.
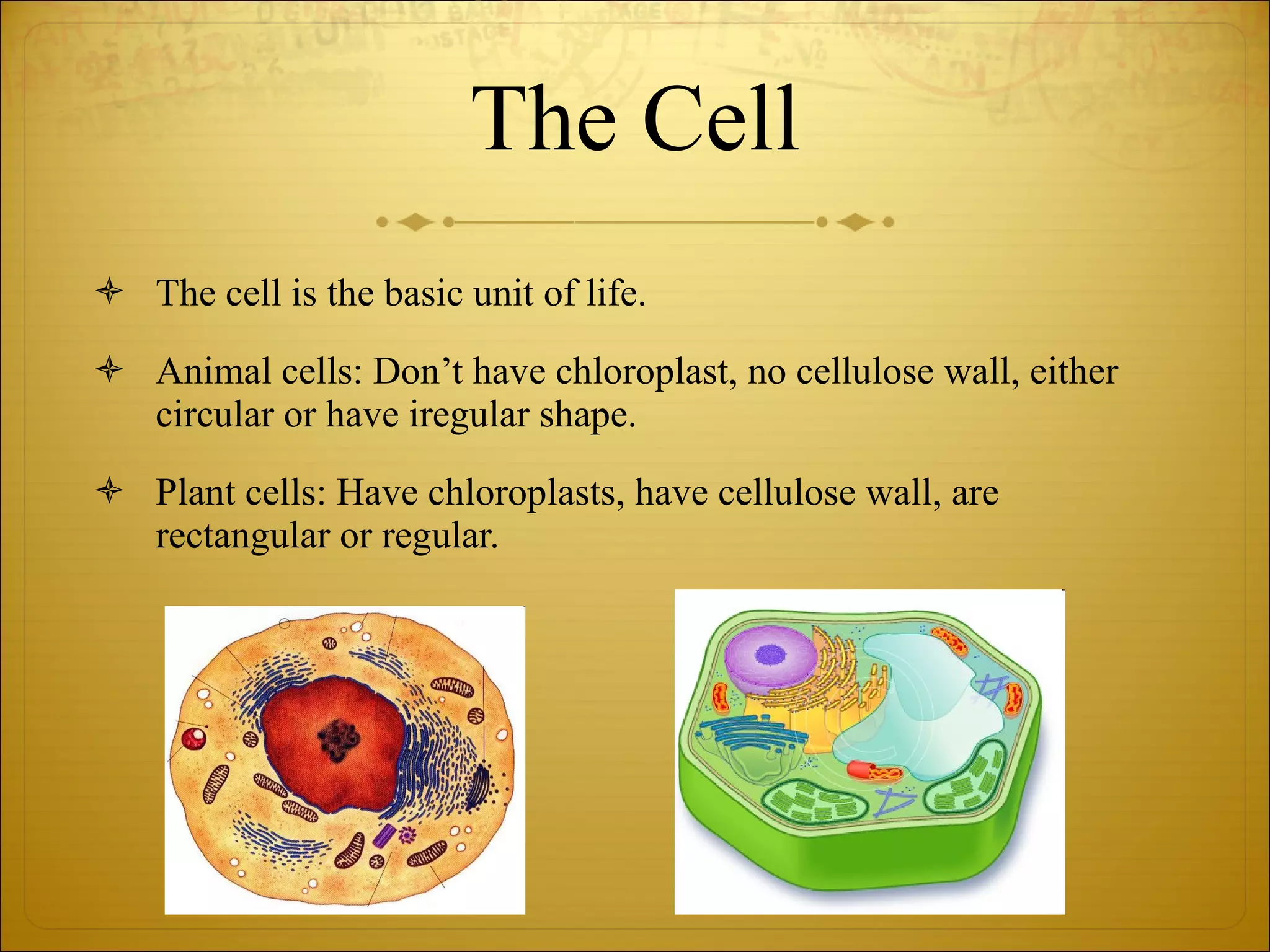
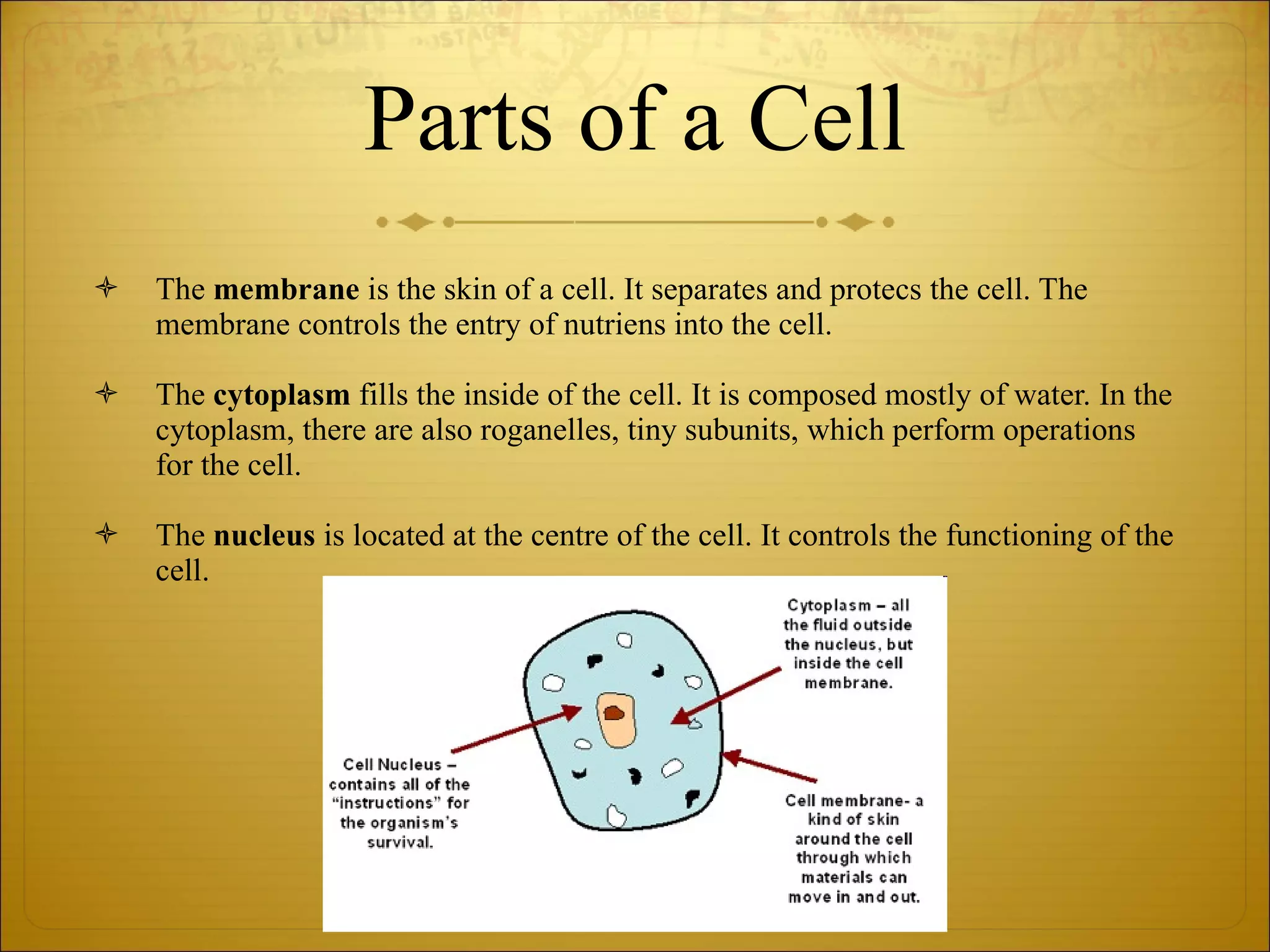
2) Cells are the basic unit of life and come in plant and animal forms with different structures and organelles.
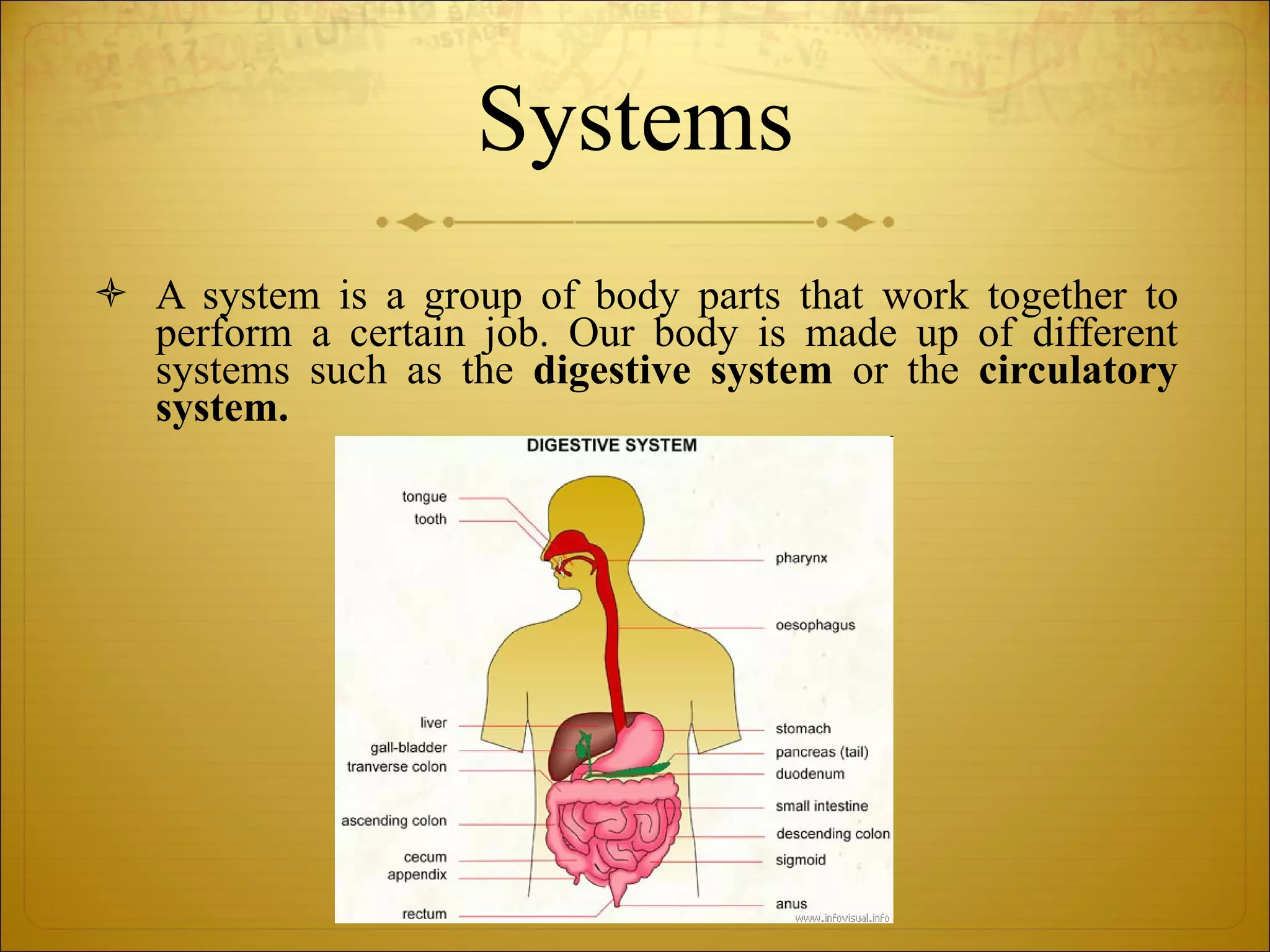
3) Organisms can be unicellular, consisting of one cell, or multicellular, made of many cell types organized into tissues, organs, and systems.