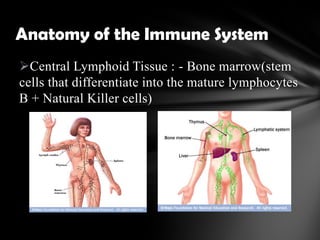
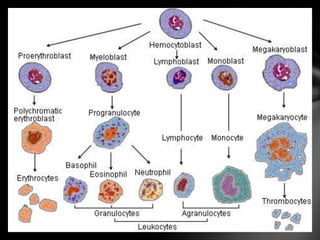
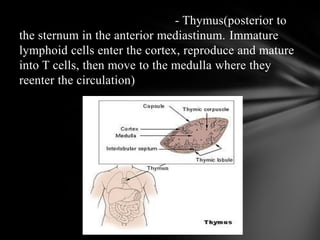
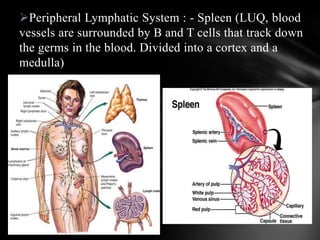
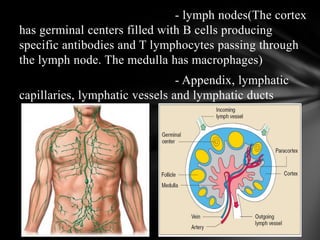
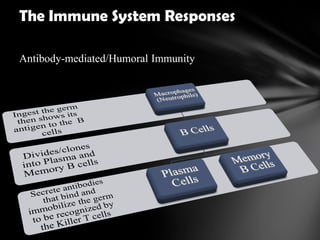
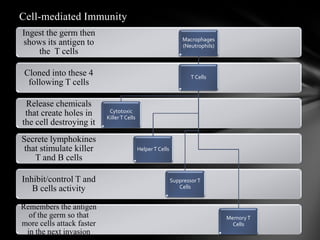
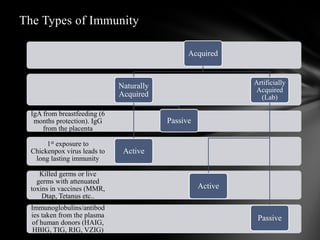
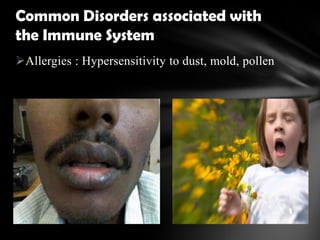
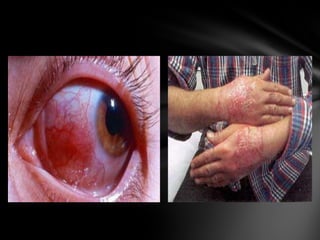
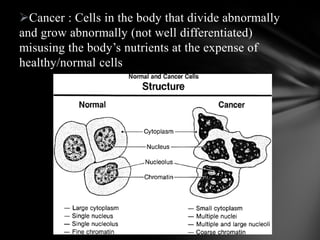
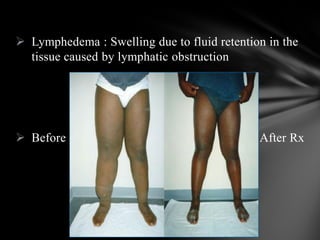
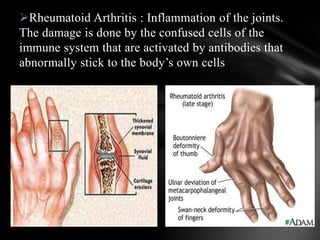
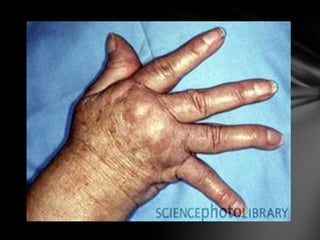
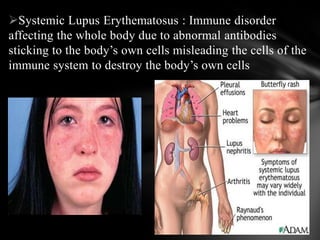
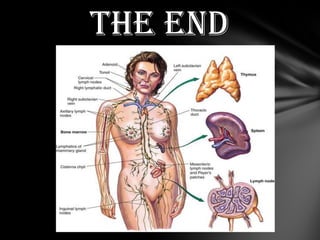
The document summarizes the anatomy and function of the immune system. It describes the central and peripheral lymphatic tissues, including the bone marrow, thymus, and spleen. It also explains the roles of T cells, B cells, macrophages, antibodies, and memory cells in mediating humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Finally, it lists some common immune disorders like allergies, anaphylaxis, cancer, chronic fatigue syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis.