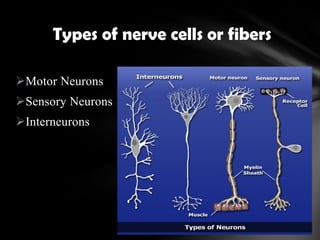
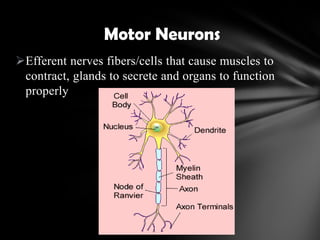
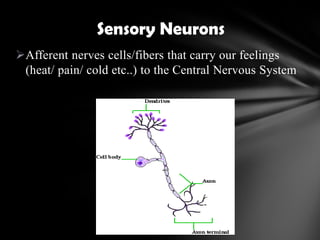
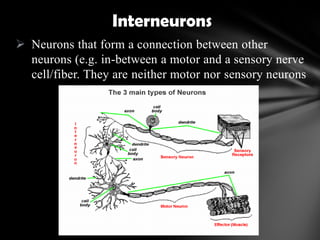
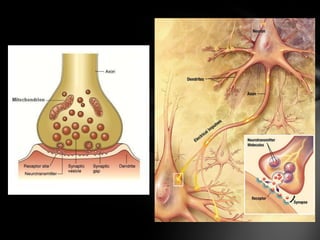
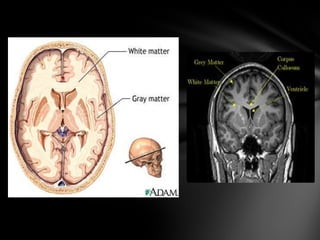
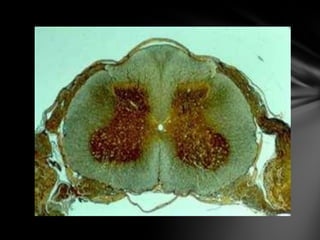
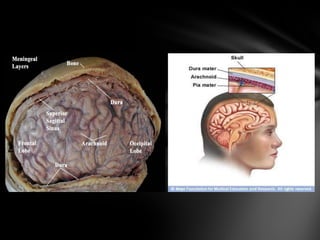
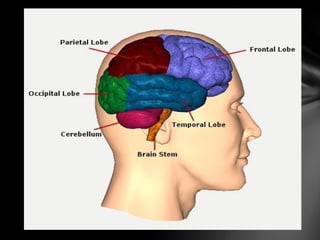
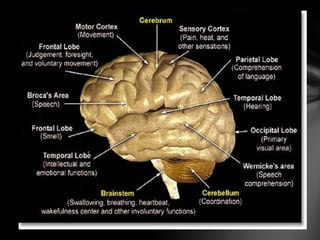
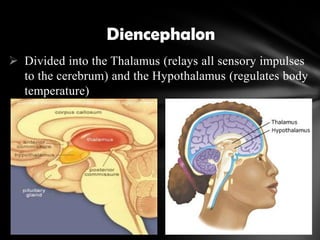
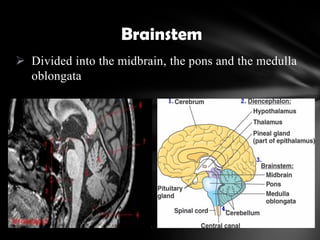
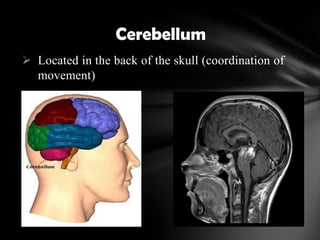
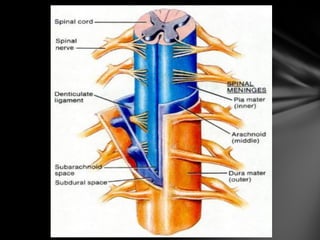
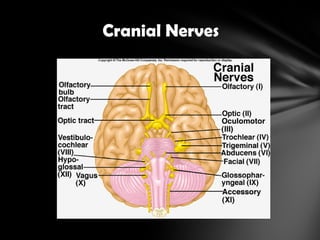
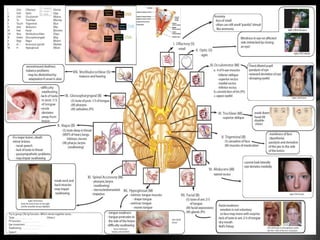
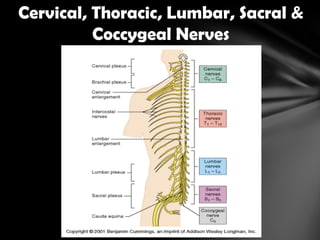
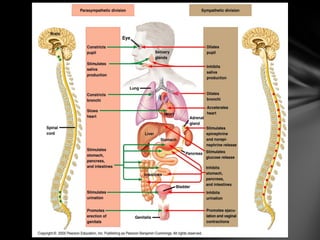
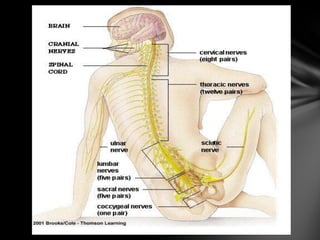
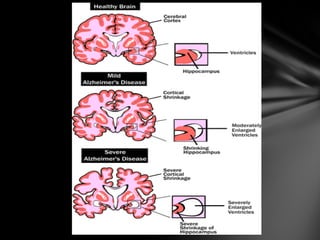
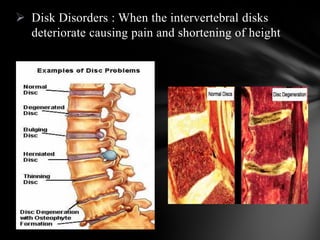
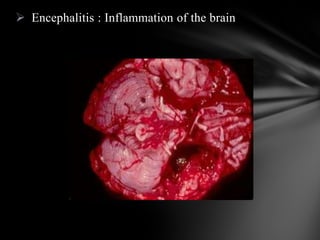
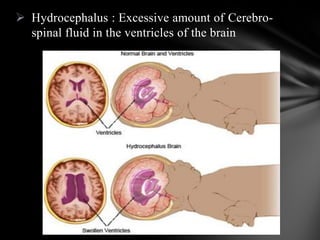
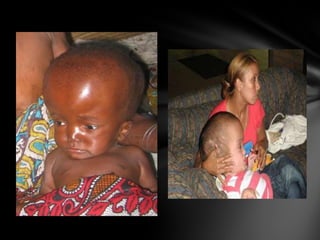
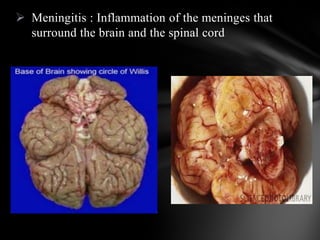
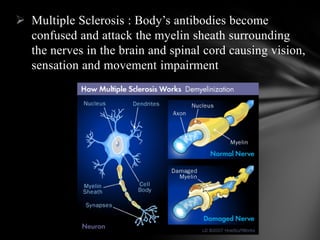
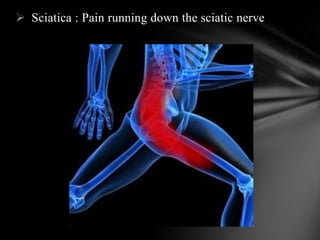
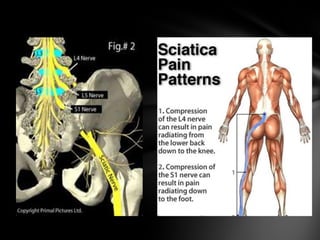
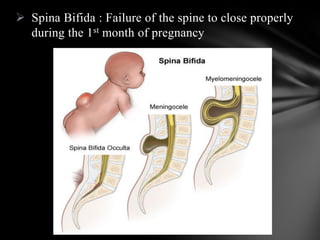
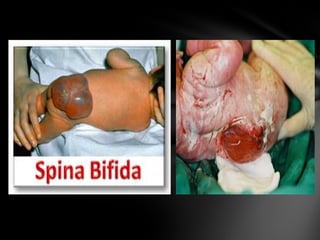
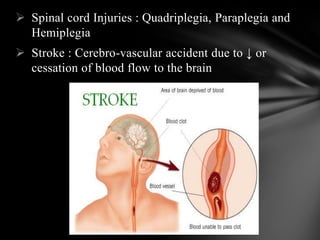
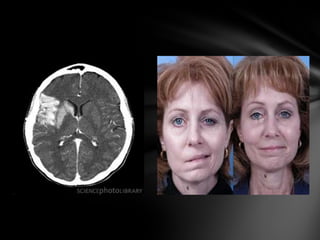
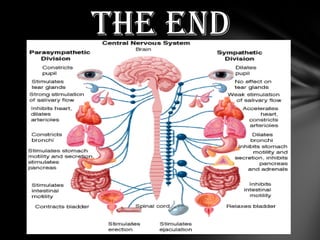
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is protected by the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. The brain is made up of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The cerebrum controls sensory and motor functions. The PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body and includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions and is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. Common disorders of the nervous system include Alzheimer's disease, ALS, epilepsy, migraines, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's