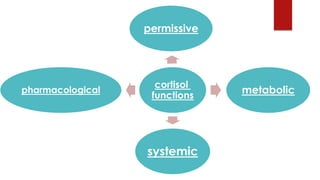
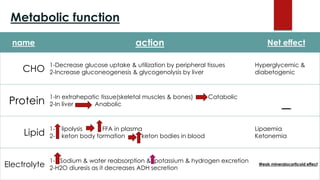
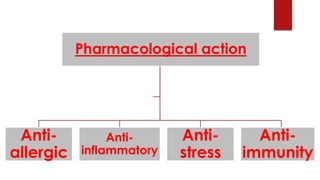
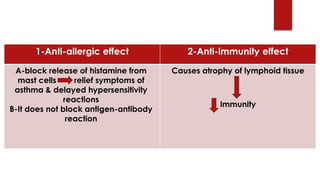
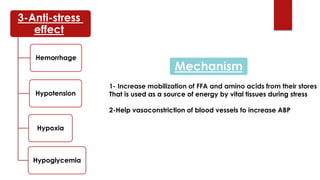
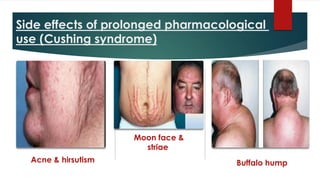
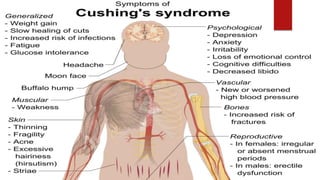
Cortisol has several important functions in the body. It acts as a permissive hormone that allows other hormones like glucagon and catecholamines to increase blood glucose levels. Cortisol also has metabolic effects like increasing blood sugar and breaking down fats and proteins. Additionally, cortisol has systemic roles in maintaining functions of the central nervous, cardiovascular, skeletal, and immune systems. Pharmacologically, cortisol acts as an anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-stress, and anti-immune hormone. Prolonged high levels of cortisol can lead to side effects like acne, weight gain, and striae.