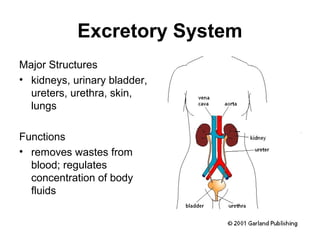
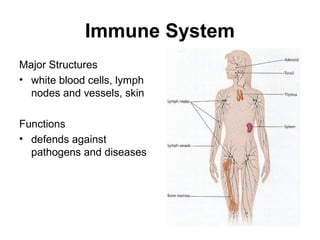
The human body is composed of 11 organ systems that work together to keep us alive. Each system is made up of major structures that carry out important functions. The organ systems include the circulatory system which transports blood throughout the body; the digestive system which breaks down food and absorbs nutrients; and the nervous system which controls the body's functions and senses the environment. Working in harmony, these 11 systems allow the human body to survive and thrive.