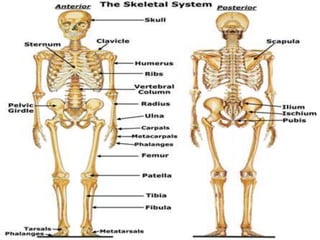
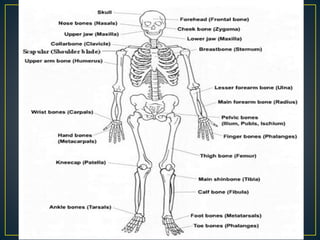
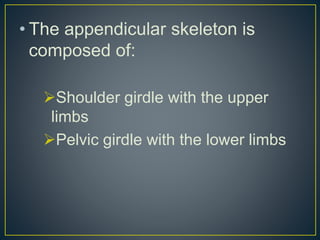
The skeletal system provides structure and support to the body through bones and joints. It is divided into the axial skeleton, including the skull, vertebral column, ribs and sternum, and the appendicular skeleton comprising the shoulder and pelvic girdles attached to the upper and lower limbs. Bones provide sites for muscle attachment, protect internal organs, contain marrow for blood cell production, and store minerals. Movement occurs in the joints but is enabled by muscle contraction and controlled largely by the will, with some involuntary actions like breathing.