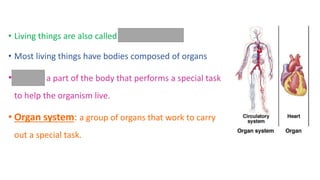
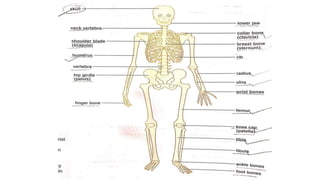
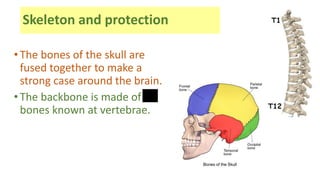
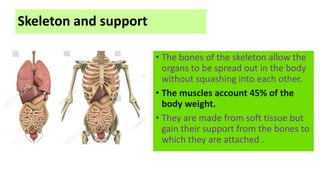
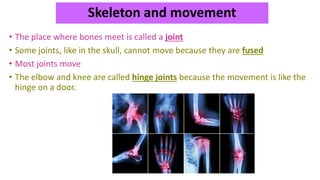
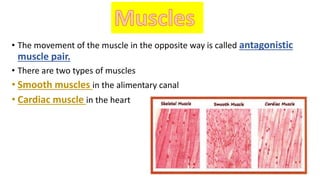
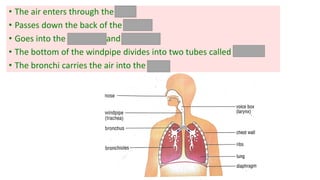
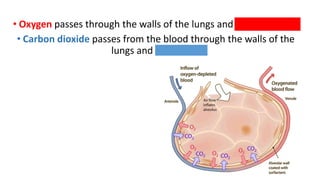
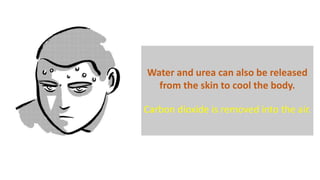
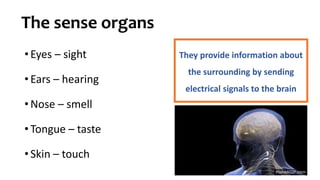
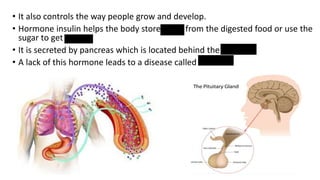
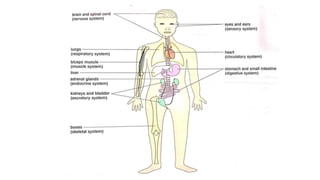
The document discusses the major organ systems of the human body. It describes 10 organ systems: skeletal, muscular, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, nervous, excretory, sensory, and endocrine systems. Each system is comprised of different organs that work together to carry out important functions needed for survival such as movement, breathing, waste removal, and hormone regulation. The skeletal system includes 206 bones that provide structure, support, and protection. The muscular system contains muscles that work with bones to enable movement.