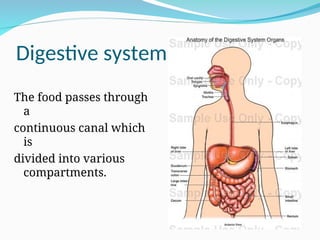
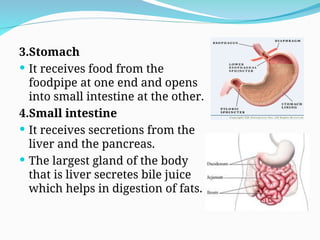
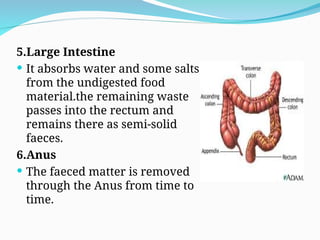
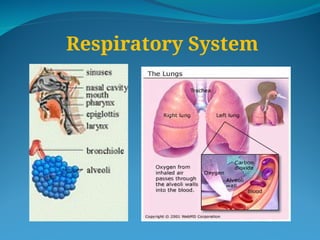
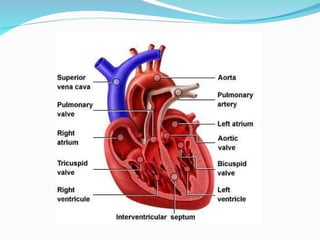
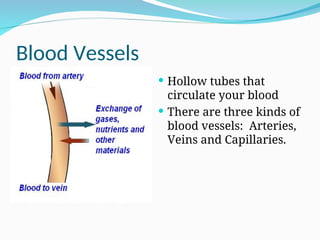
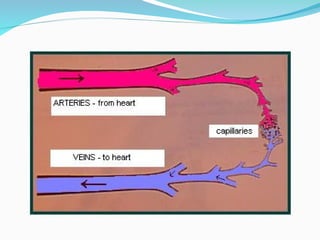
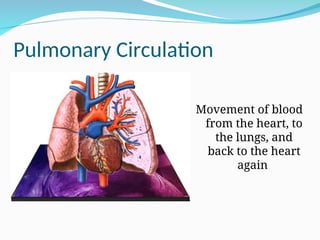
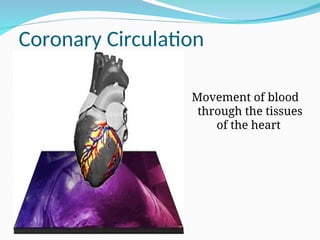
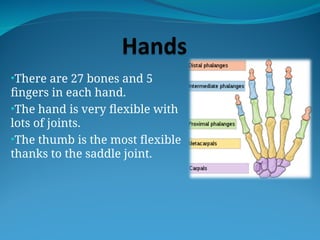
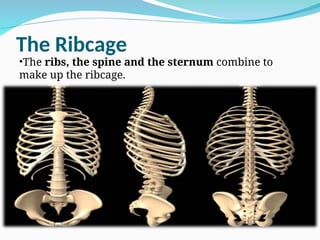
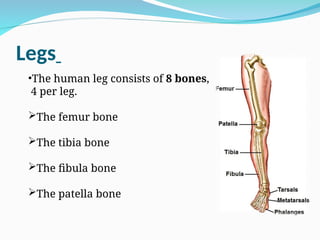
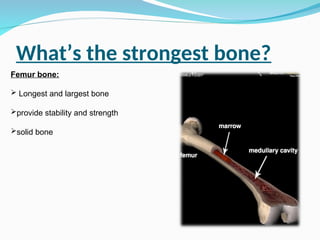
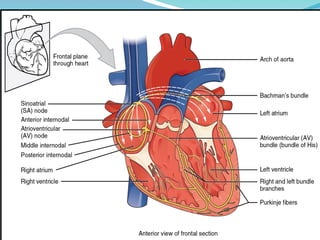
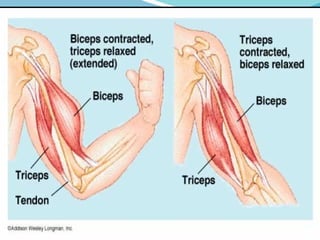
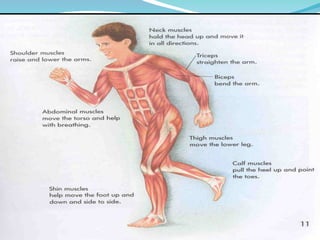
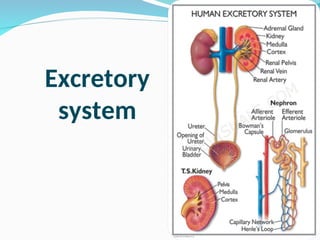
The document outlines the basic structures and functions of various human organ systems including the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, skeletal, muscular, and excretory systems. It provides detailed descriptions of each system's components and functions, emphasizing the vital roles they play in maintaining health and homeostasis. Additionally, the document highlights potential diseases related to the skeletal system and the various forms of muscles in the muscular system.