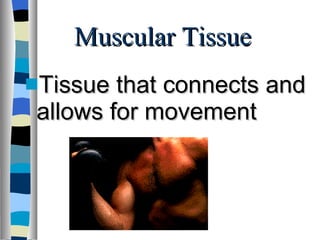
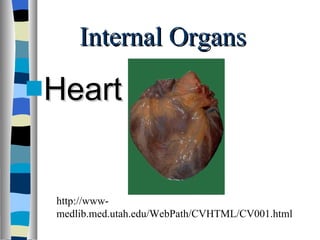
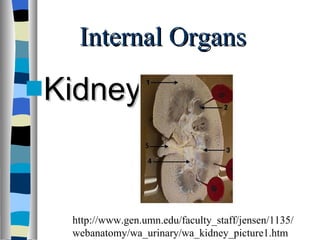
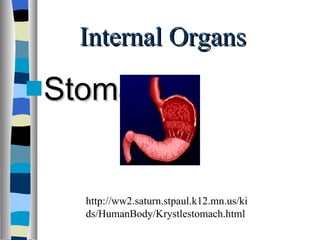
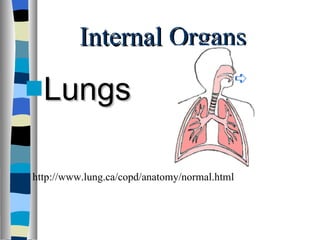
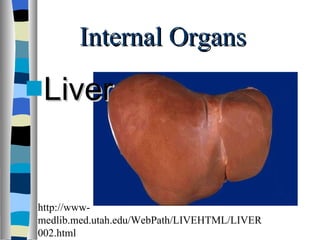
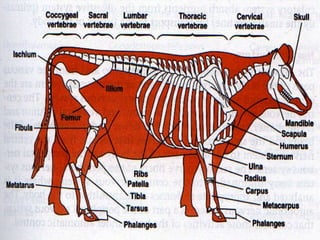
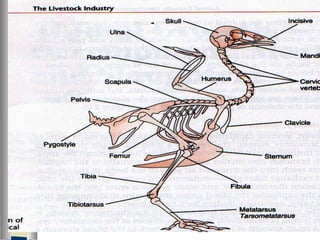
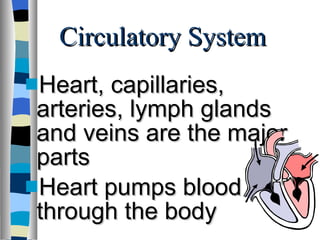
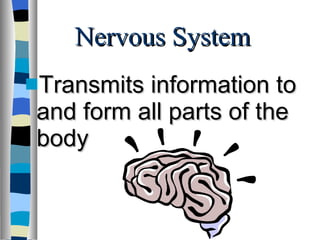
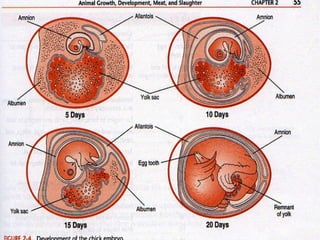
The document discusses the structure and function of various animal tissues and organ systems. It describes the main tissue types - muscular, connective, nerve, epithelial and fluid tissues - and how they combine to form organs like the heart, kidneys, stomach and lungs. It also examines the circulatory, nervous, endocrine, urinary, respiratory, and muscular systems. Reproduction and embryonic development in livestock are covered as well. The structure of meat is discussed, noting its main components of muscle, fat, bone and connective tissue.