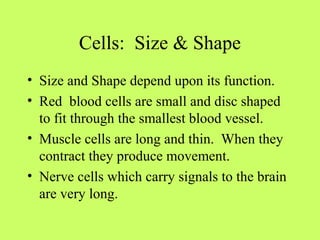
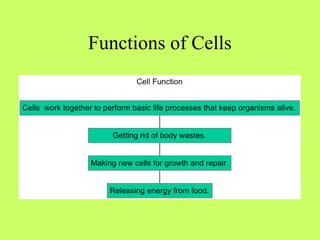
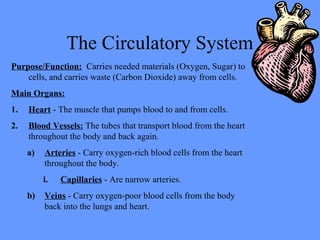
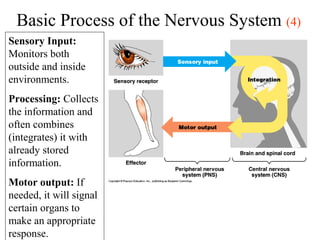
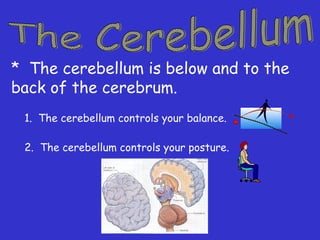
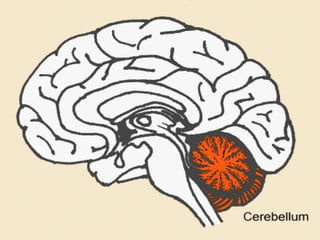
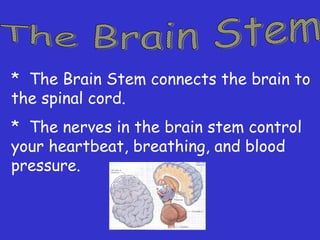
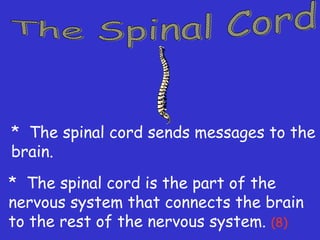
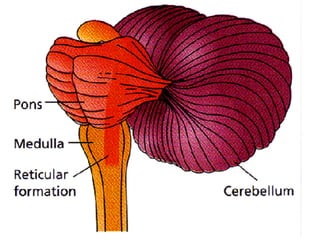
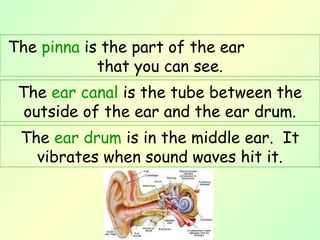
The document provides information about the nervous system and its main components. It discusses (1) how the nervous system controls all activities of the body, (2) the central nervous system which includes the brain and spinal cord as the control center, and (3) the outer nervous system which connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body using nerves and sense organs. The brain is divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem which each have specific functions. The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the nervous system and carries messages throughout the body.