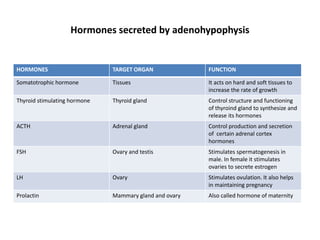
The endocrine system includes glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The major glands are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which is called the "master gland" as it regulates the activity of other glands by producing hormones like TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH. Other glands like the thyroid, adrenals, and gonads produce hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and sexual development and functions.