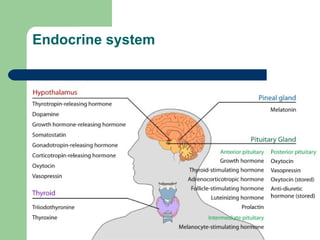
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate bodily functions. It works more slowly than the nervous system but has prolonged effects lasting hours to weeks. Hormones produced by endocrine glands control metabolism, growth, tissue function, and mood. The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is called endocrinology.