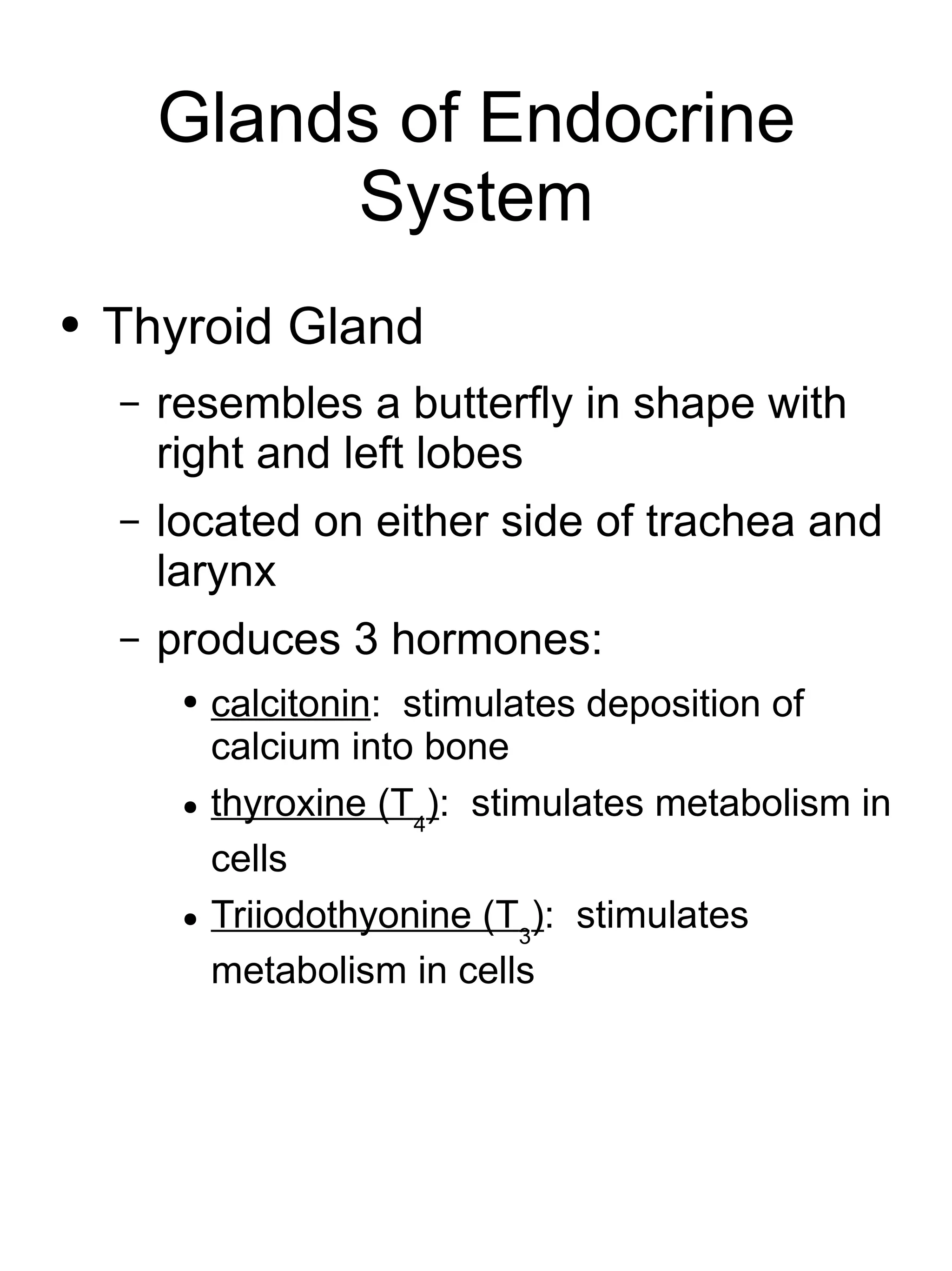
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate many body activities. The major glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and thymus gland. Each gland produces unique hormones that target specific organs to increase or decrease activity levels and regulate growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other bodily functions.