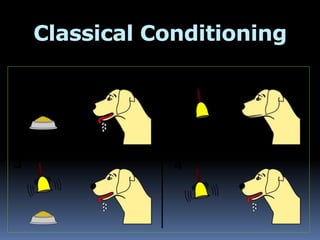
Behaviorism is a movement in psychology that views learning as occurring through interactions between organisms and their environment. It proposes three major types of learning: classical conditioning, in which a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a response; operant conditioning, where behaviors are strengthened or weakened through reinforcement and punishment of consequences; and social learning theory, where observation of models leads to imitation of behaviors.