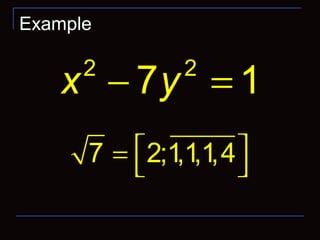This document summarizes continued fractions and their applications in number theory and combinatorial game theory. It defines general and simple continued fractions and explains how they can represent rational and irrational numbers. Finite simple continued fractions uniquely represent rational numbers, while infinite simple continued fractions represent irrational numbers. Continued fractions can be used to solve Pell's equation and find integer solutions. The document provides examples of representing numbers like π and√2 as continued fractions and using convergents of the continued fraction of √2 to solve the Pell equation x2 - 2y2 = 1.


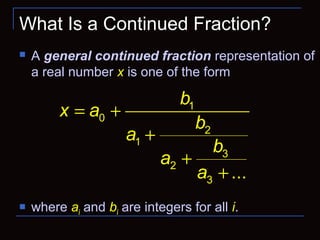
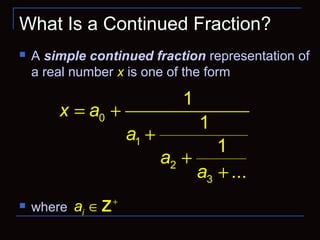
![Notation
Simple continued fractions can be written as
or
[ ]0 1 2; , ,...x a a a=
0
1 2
1 1
...x a
a a
= +
+ +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-5-320.jpg)

![Finite Simple Continued Fraction
0ia >
0
1 2
1 1 1
...
n
x a
a a a
= +
+ +
[ ]0 1 2; , ,..., nx a a a a=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-7-320.jpg)
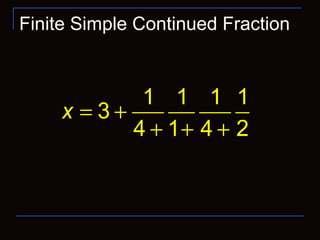







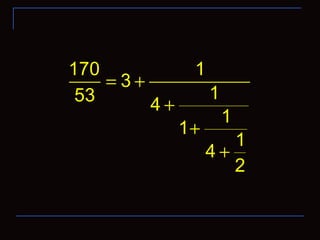

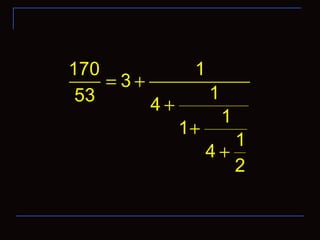
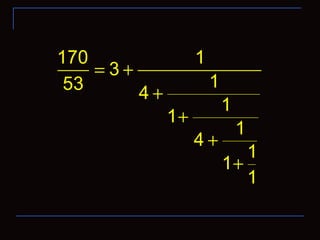
![[ ] [ ]
170
3;4,1,4,2 3;4,1,4,1,1
53
= =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-20-320.jpg)





![Finding The Continued Fraction
[ ]
19
0;2,1,2,6
51
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-26-320.jpg)

![Infinite Simple Continued Fraction
0ia >
0
1 2
1 1
...x a
a a
= +
+ +
[ ]0 1 2; , ,...x a a a=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-28-320.jpg)

![Infinite Simple Continued Fraction
[ ]3;7,15,1,292,...π =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-30-320.jpg)
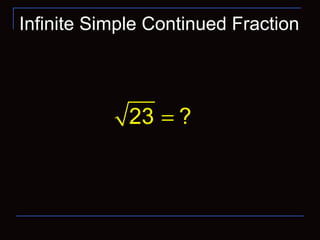






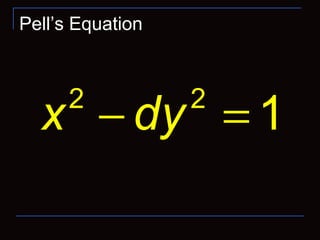
![Definition
The continued fraction made from
by cutting off the expansion after the kth
partial denominator is called the kth
convergent of the given continued fraction.
[ ]0 1 2; , ,...x a a a=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-39-320.jpg)
![Definition
In symbols:
[ ]0 1 2; , ,... ,1k kC a a a a k n= ≤ ≤
0 0C a=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecontinuedfractionparti-130509181414-phpapp01/85/The-continued-fraction-part-i-40-320.jpg)