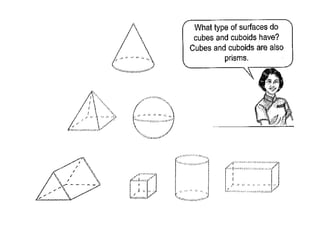
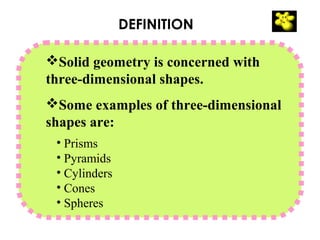
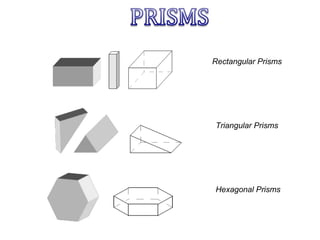
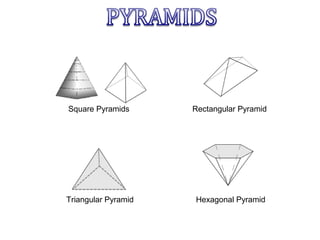
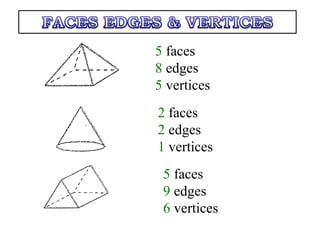
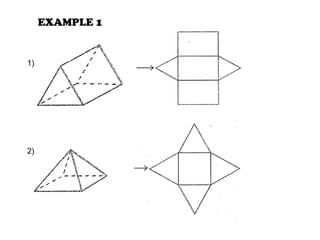
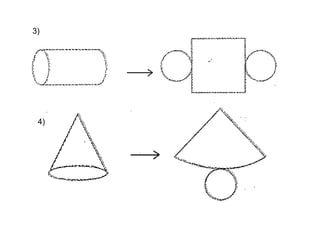
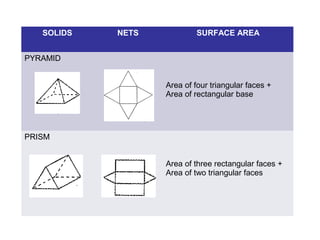
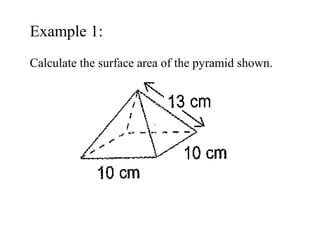
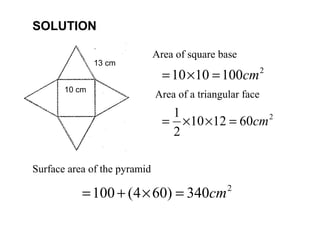
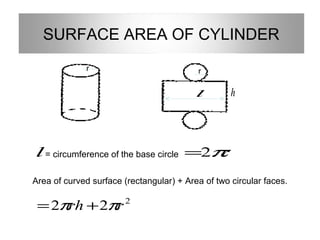
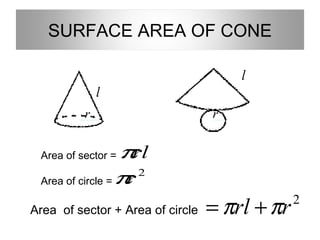
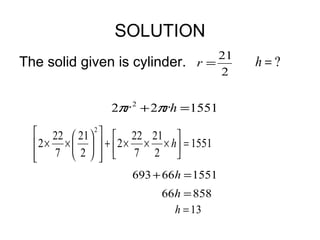
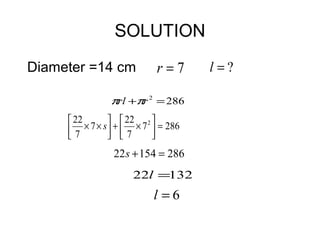
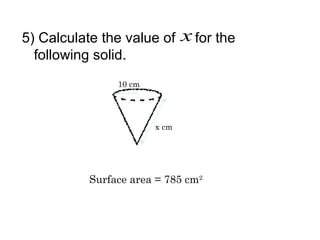
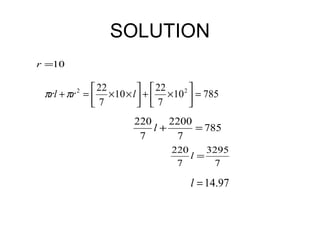
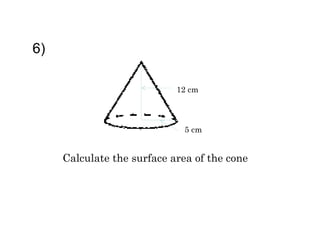
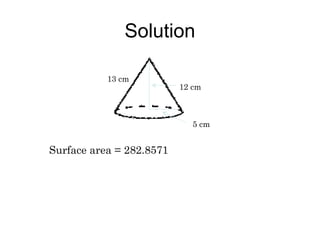
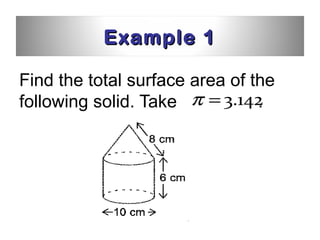
This document provides information about solid geometry, including definitions of different 3D shapes like prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. It describes their key properties and provides examples. It also discusses nets, which are 2D shapes that can be folded into 3D solids. The document then covers calculating the surface areas of different solids and provides examples of solving surface area problems for prisms, cylinders, cones, and spheres. It concludes with practice problems for students to calculate surface areas.