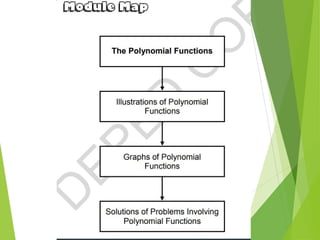
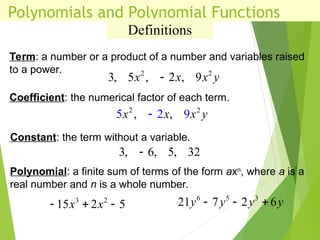
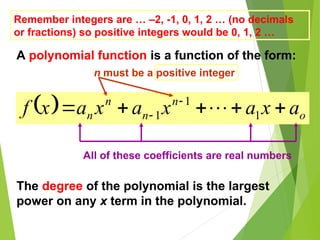
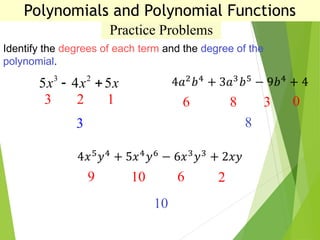
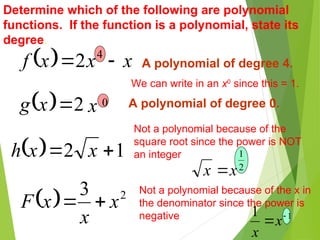
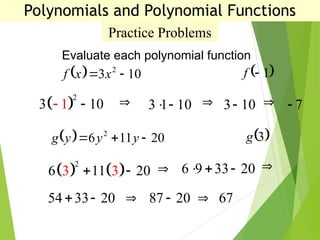
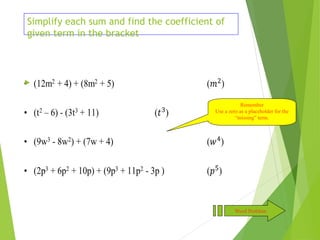
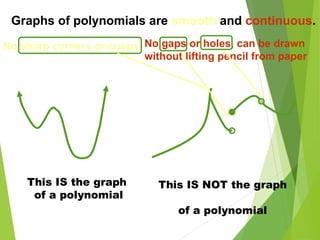
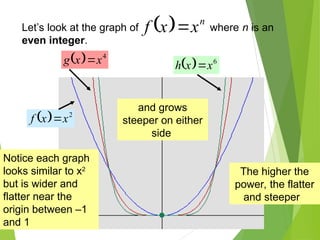
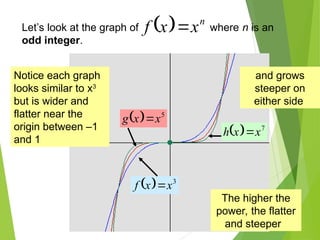
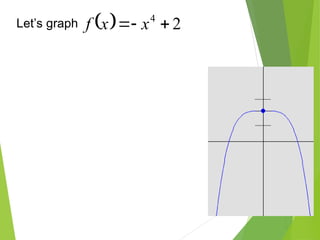
The document defines polynomials and polynomial functions, noting the importance of coefficients, degrees, and the distinction between polynomial and non-polynomial functions. It provides practice problems for identifying degrees, evaluating functions, and understanding the graphs of polynomials. The behavior of graphs for even and odd degrees is discussed, emphasizing their smooth and continuous nature.