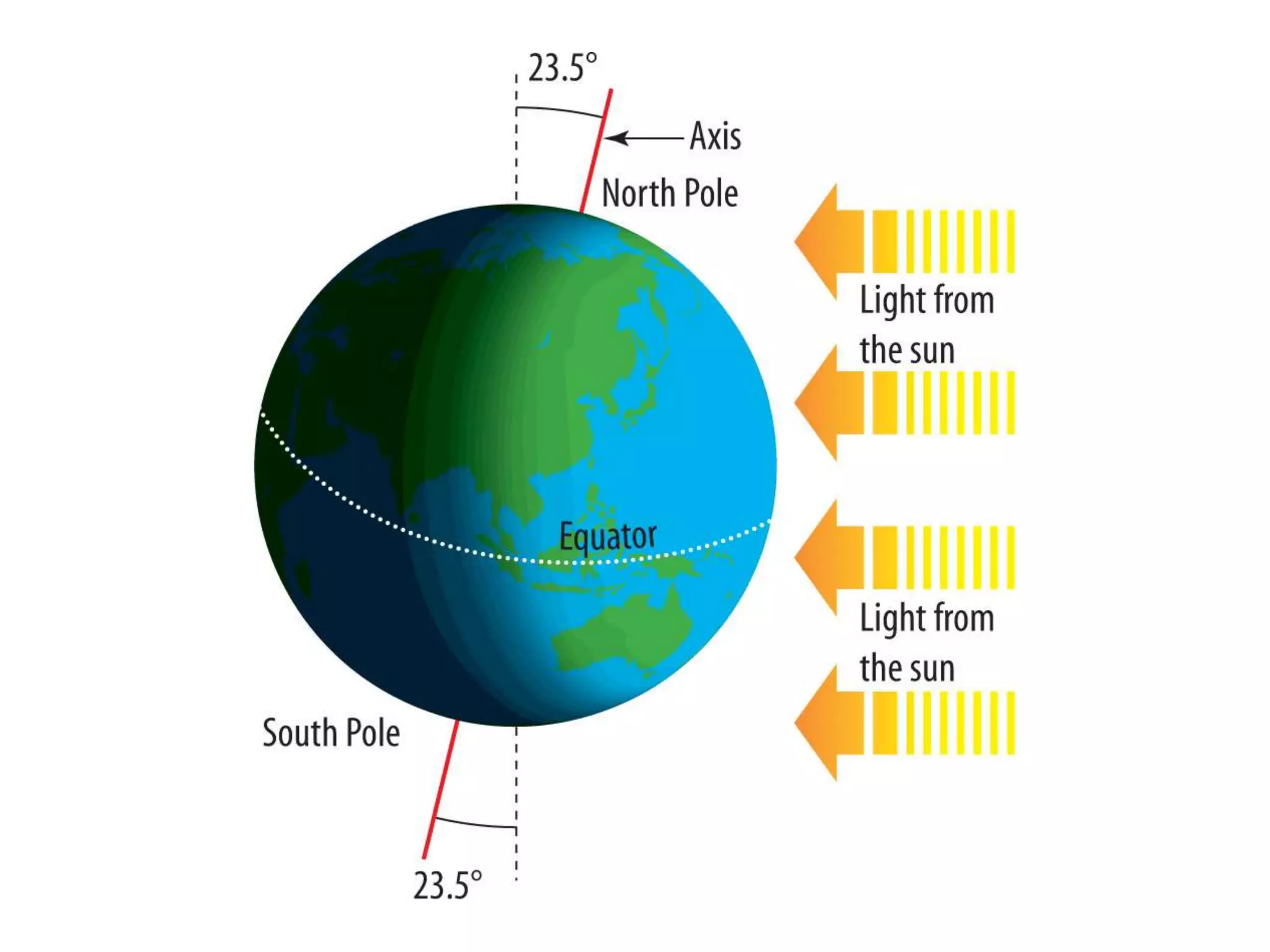
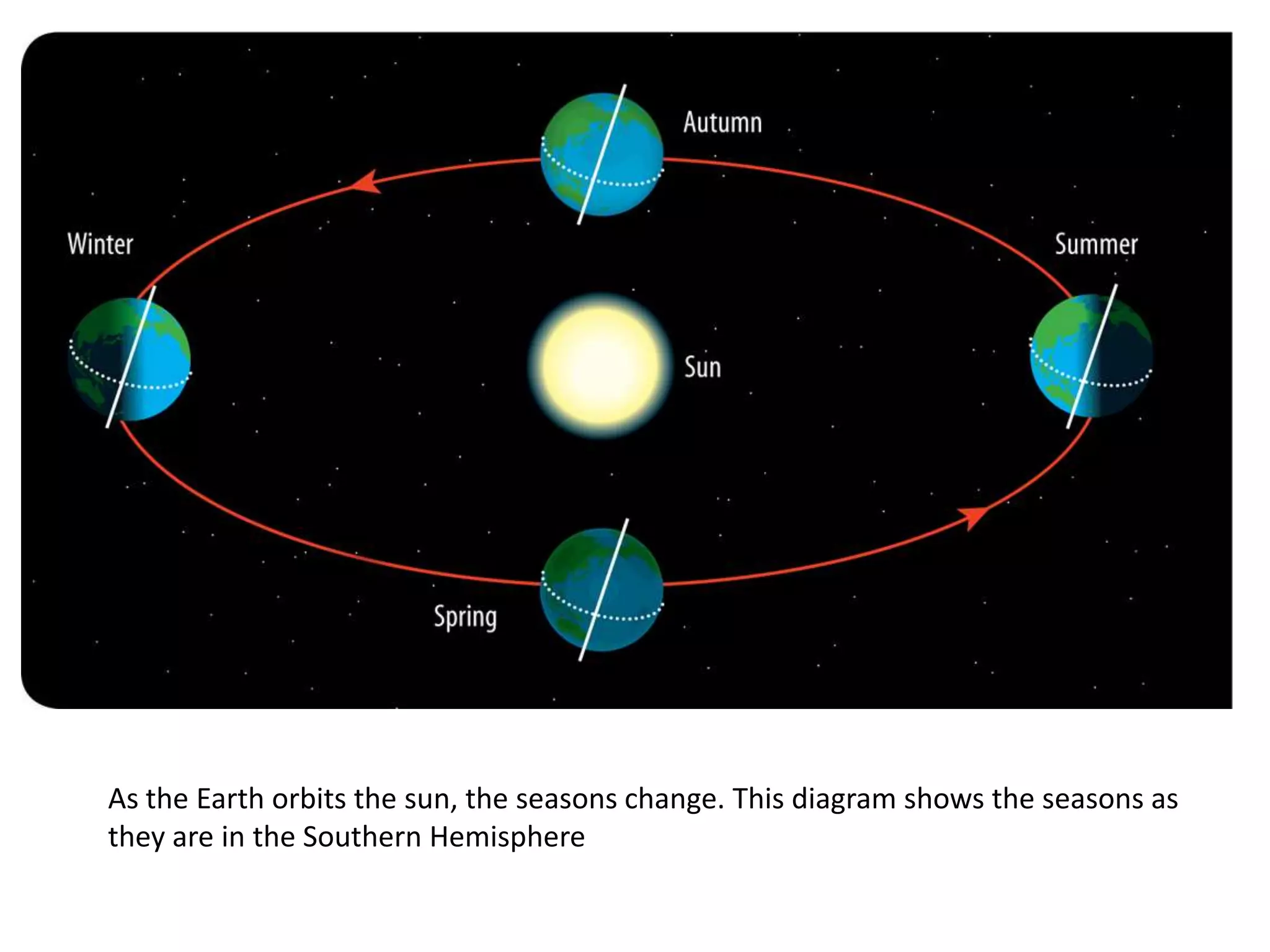
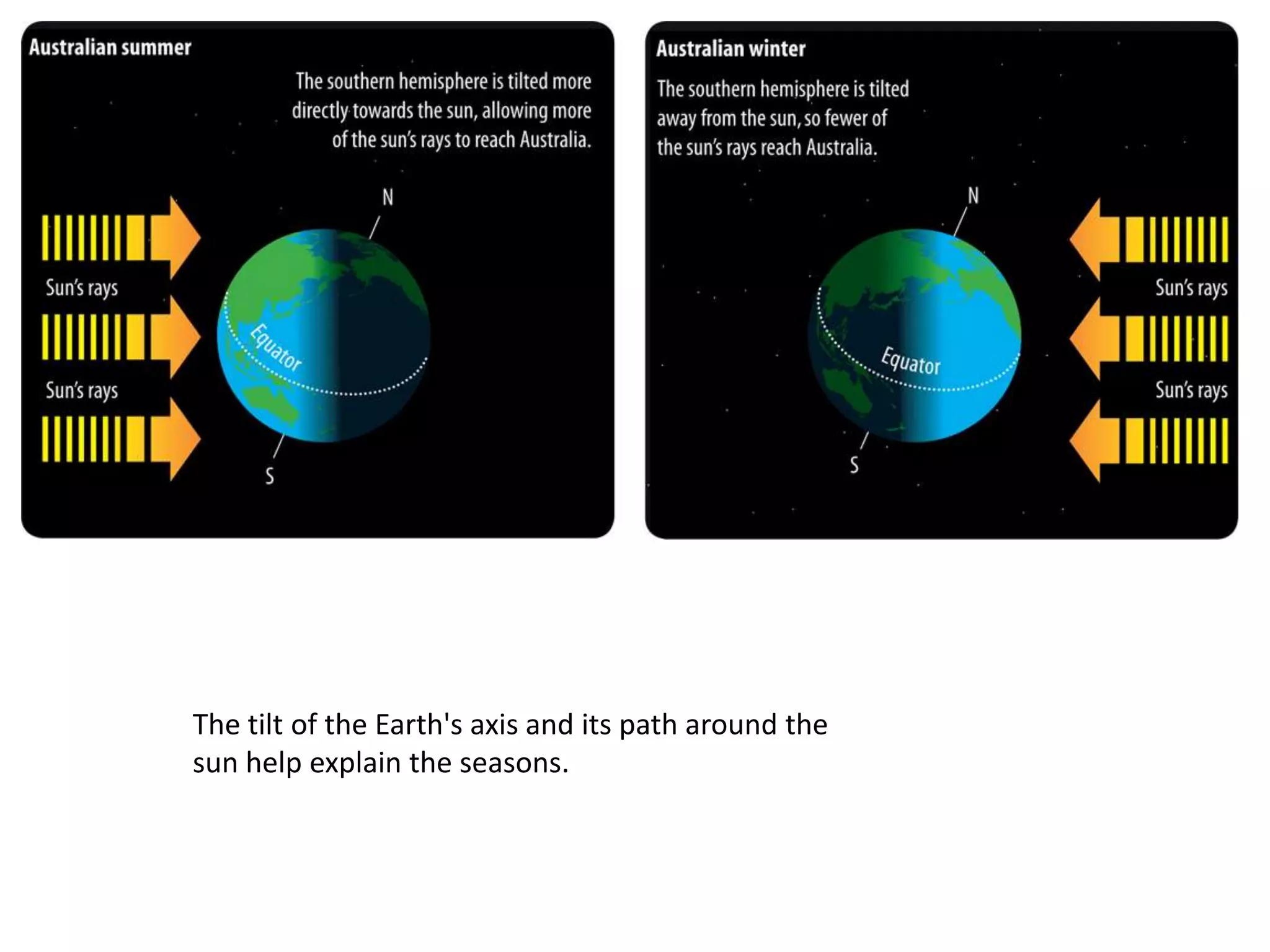
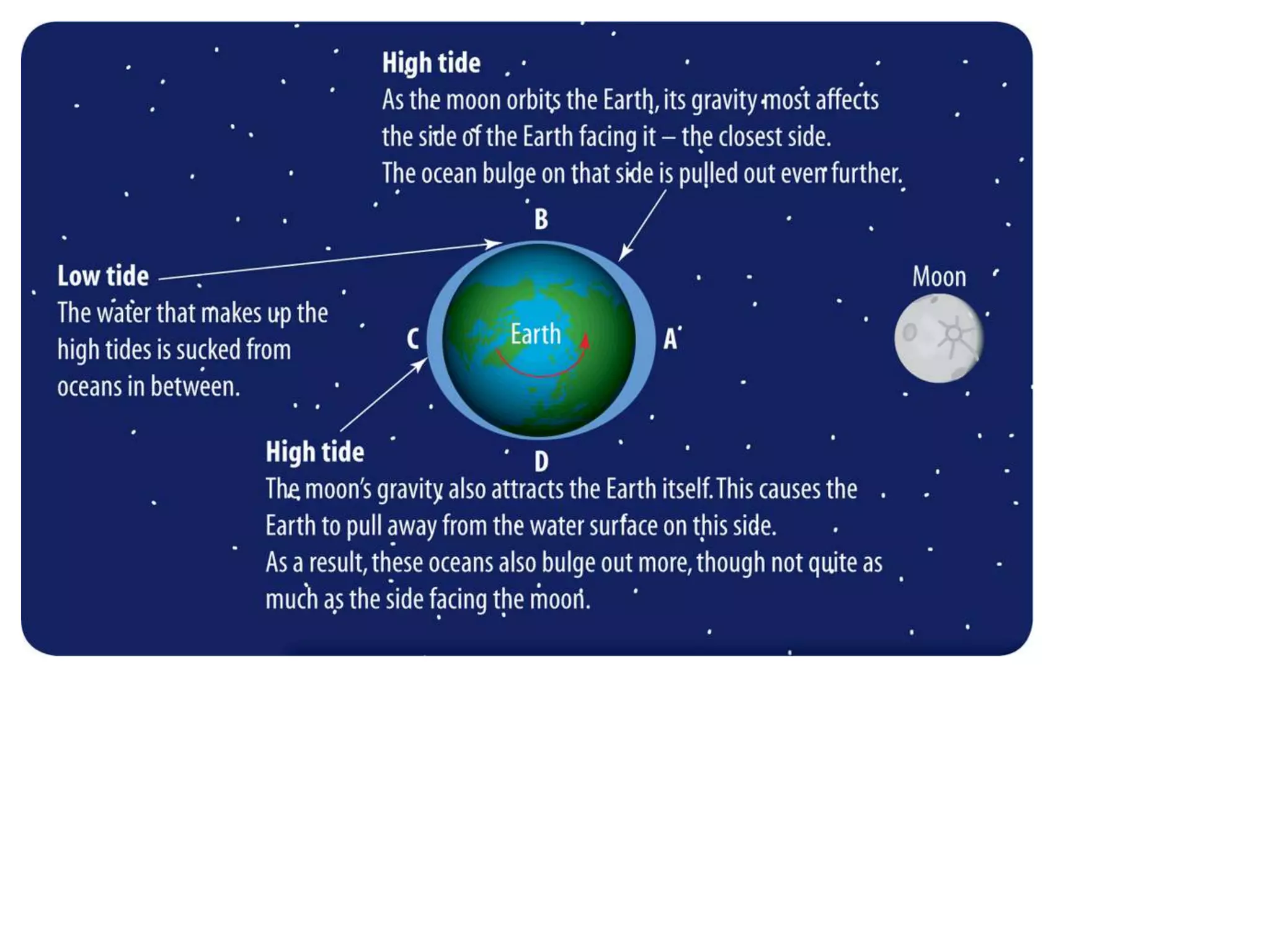
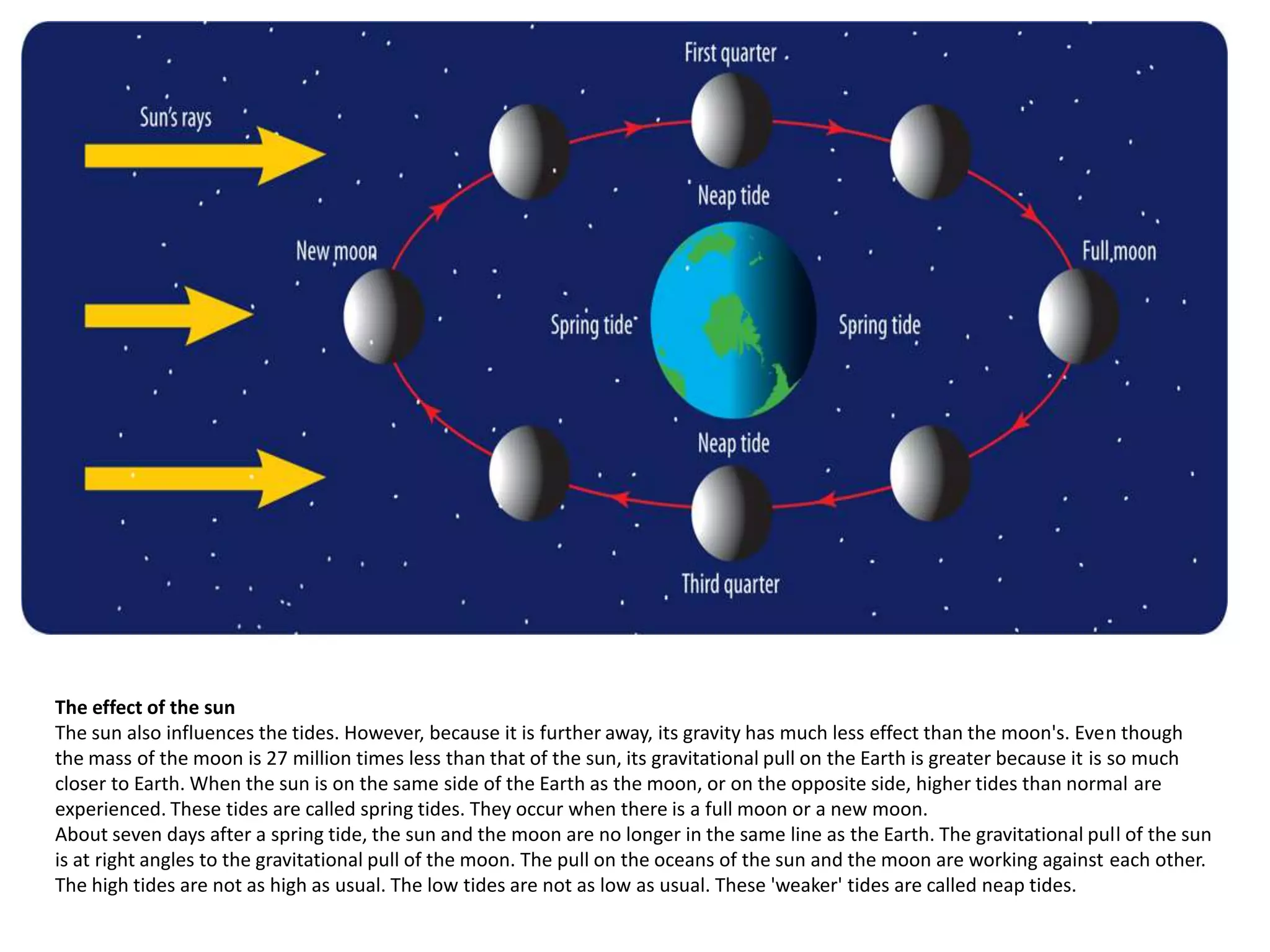
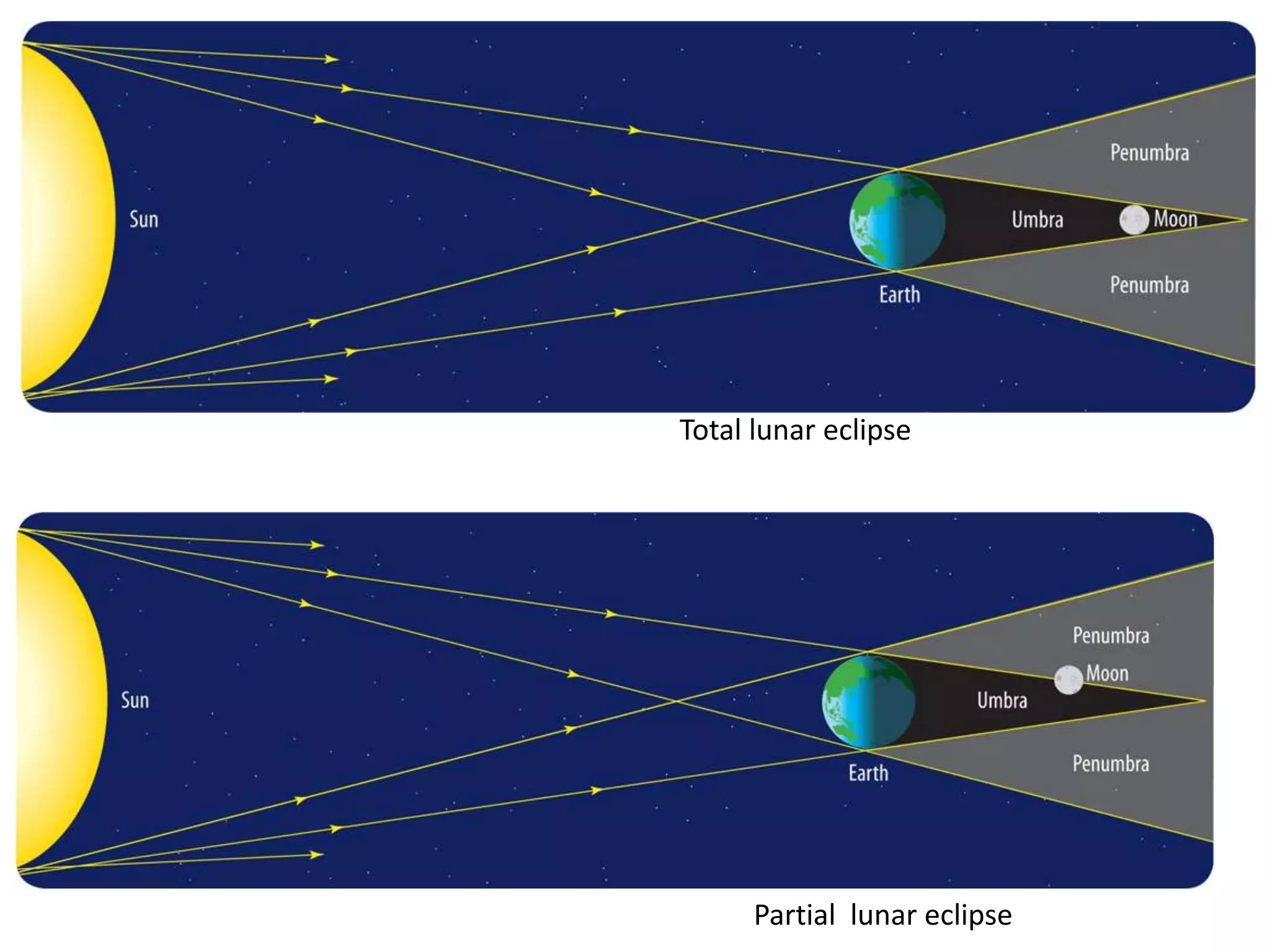
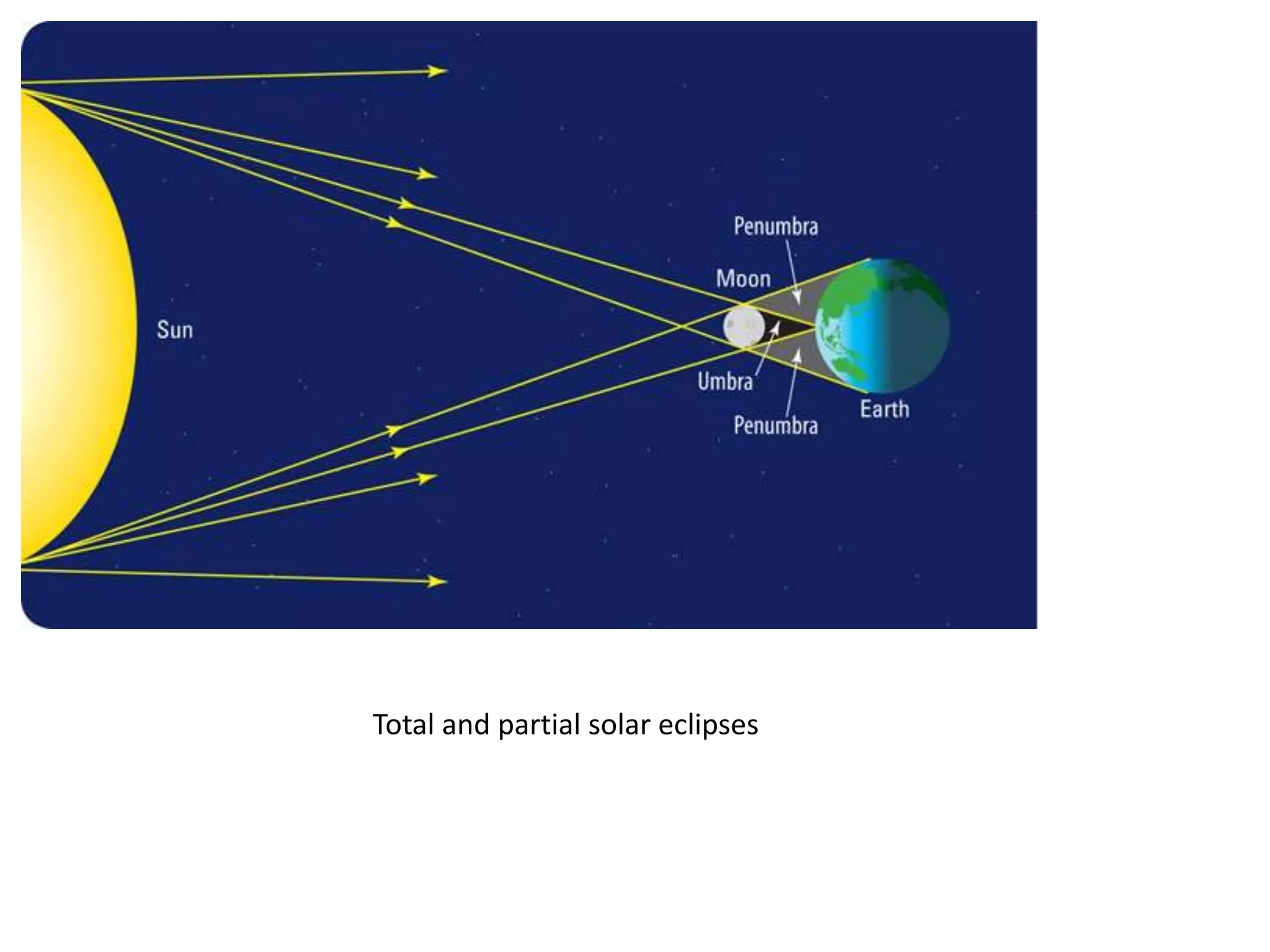
The document discusses the relationship between the Earth, moon, and sun. It explains that the Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun cause the seasons to change. As the Earth orbits, different hemispheres are tilted toward or away from the sun, resulting in summer and winter. It also describes how the gravitational pull of the moon causes ocean tides, with the highest tides occurring during full moons and new moons. Additionally, it explains lunar and solar eclipses, noting that a solar eclipse can only occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the Earth and sun.