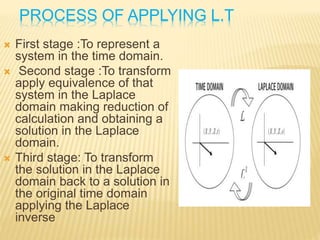
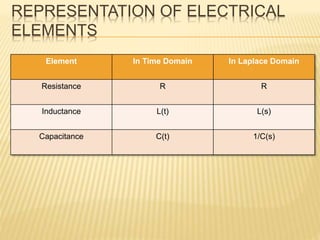
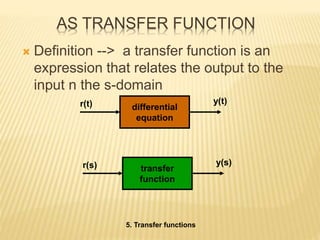
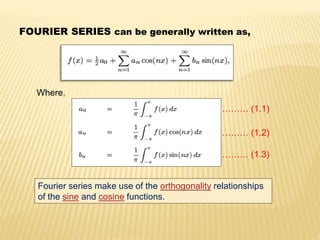
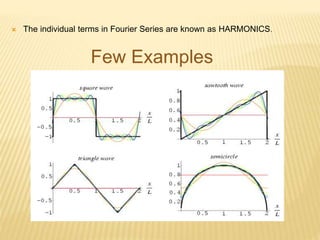
This document discusses different mathematical concepts including Laplace transforms, Fourier series, and their applications. It defines Laplace transforms as a linear operator that transforms a function of time into a function of complex variables. Laplace transforms can be used to solve differential equations by converting them into algebraic equations. Fourier series represent periodic functions as the sum of simple sine and cosine terms. Both Laplace transforms and Fourier series have applications in electrical engineering for analyzing circuits, signals, and systems. Overall, the document outlines important mathematical concepts and their uses in engineering problems.