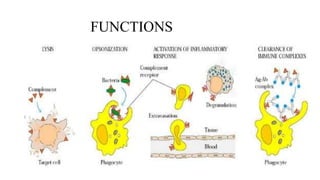
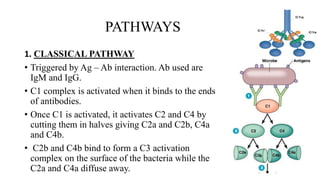
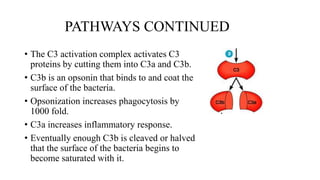
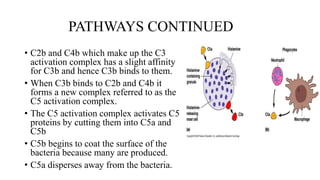
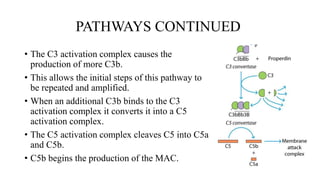
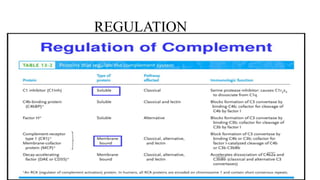
The complement system is part of the innate immune system that enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells. It consists of over 30 proteins and fragments produced by the liver and found in blood serum. There are three pathways of complement activation: the classical pathway triggered by antibody-antigen interaction, the lectin pathway triggered by mannose-binding lectin, and the alternative pathway triggered by spontaneous activation of complement proteins. All three pathways result in the formation of the membrane attack complex that causes cell lysis. Complement deficiencies are associated with increased susceptibility to certain bacterial infections.