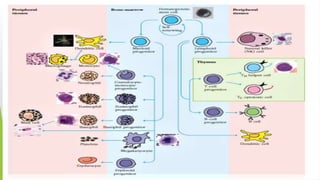
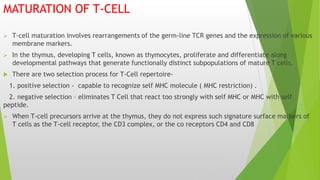
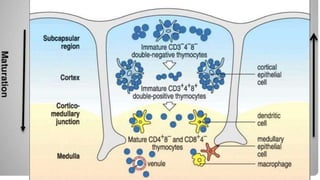
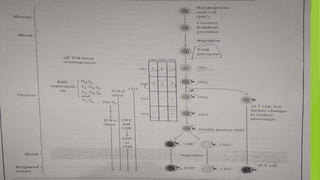
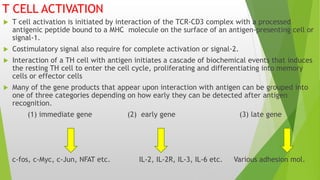
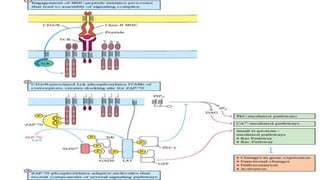
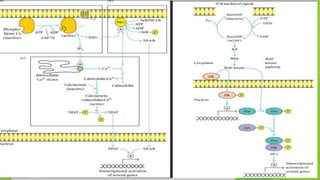
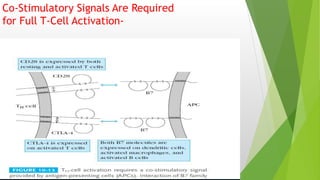
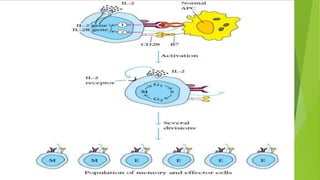
This document summarizes the key stages in T-cell maturation, activation, and differentiation. It discusses how T-cells mature in the thymus through positive and negative selection to screen for self-MHC restriction and eliminate self-reactive cells. Activation requires signal 1 through TCR-antigen-MHC interaction and signal 2 via co-stimulatory molecules. Upon activation, T-cells can proliferate and differentiate into memory cells or effector cells. CD4 and CD8 T-cells leave the thymus as naive cells and, upon antigen recognition, can become activated and further differentiate.