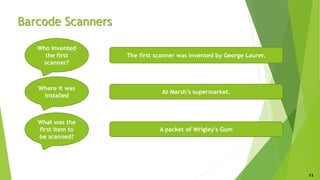
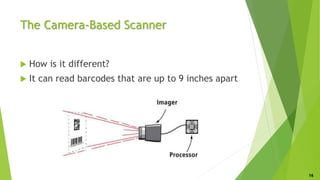
This document discusses the history, types, and applications of barcodes, focusing on various forms such as UPC and QR codes. It details the evaluation process for barcodes, including criteria for their effectiveness, and the invention of barcode scanners. The conclusion emphasizes the efficiency and time-saving benefits that barcodes have brought to businesses and retail shopping.