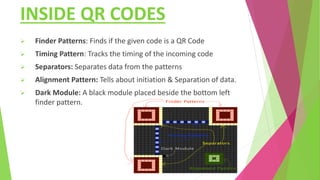
This document provides an overview of barcode and QR code technology. It discusses that barcodes store data in linear/1D format while QR codes store data in 2D, allowing it to hold more information. The document outlines the basic components and workings of barcodes and QR codes, their advantages like unique identification and accuracy, and applications in areas like libraries, laboratories, and industry. QR codes in particular can be scanned by any smartphone and are commonly used now for linking to URLs and automated text/SMS.