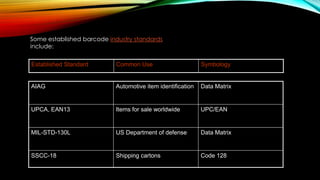
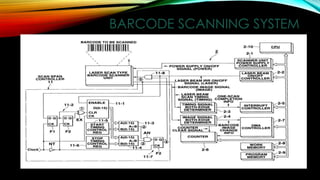
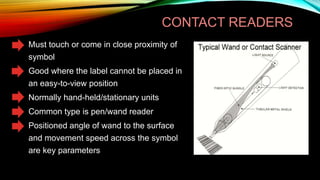
The document provides an overview of barcodes, including their history, technology, terminology, types, uses and benefits. It discusses that the first barcode patent was issued in 1952 and how they started being used widely in grocery stores in the 1970s to automate checkout processes. Barcodes represent a unique product identity and allow for accurate, real-time data collection that saves labor costs and improves resource management. Common barcode types include UPC, Code 128 and Data Matrix, which are used across various industries like retail, shipping, warehousing and healthcare for applications like inventory tracking, electronic data interchange and patient identification.