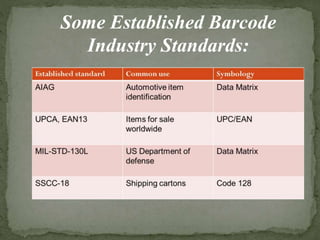
Barcodes and barcode readers provide benefits of speed, accuracy, and data integrity when used for identification and tracking of items. Barcodes represent alphanumeric data as patterns of bars and spaces that can be scanned by various types of barcode readers, including pen, slot, CCD, and laser scanners. While barcodes have widespread applications and advantages, disadvantages include potential system failures affecting delays and issues reading damaged or poor quality barcodes.