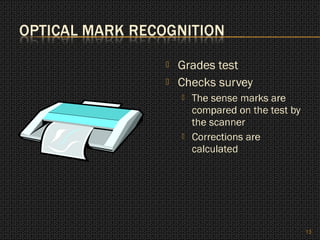
The document discusses different types of scanners and how they work. It describes flatbed scanners, portable scanners, and sheetfed scanners. It also covers optical scanners, bar code readers, MICR, OCR, and OMR. Uses of scanners include copying documents, transmitting faxes, including images in documents, and analyzing text and images through character recognition.