Embed presentation
Downloaded 179 times


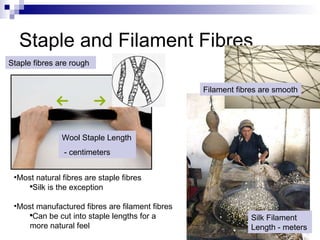


The document discusses different types of textile fibers including natural fibers like cotton, wool, silk, and flax that come from plants and animals as well as manufactured fibers such as polyester, rayon, nylon, and acetate. It describes fiber characteristics like durability, elasticity, and absorbency. It notes that most natural fibers are staple fibers of varying lengths while silk is a filament fiber and most manufactured fibers are also filament fibers that can be cut into staple lengths.





