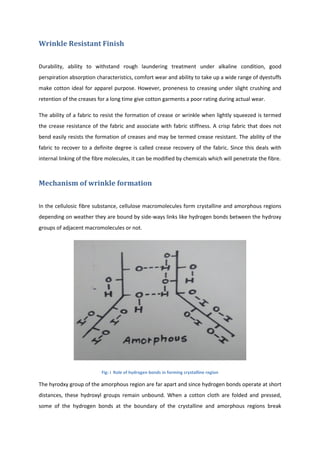
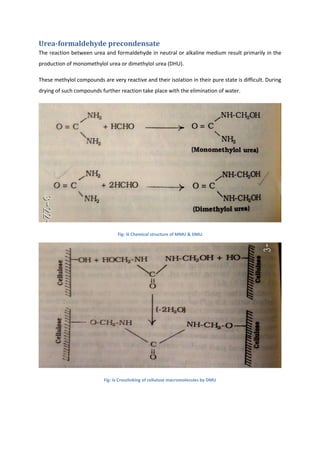
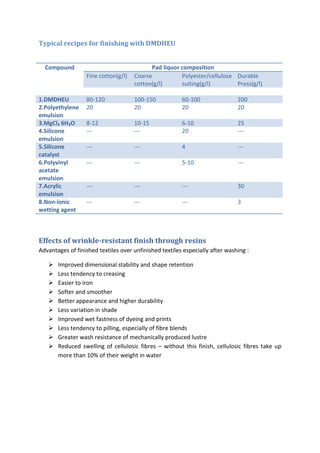
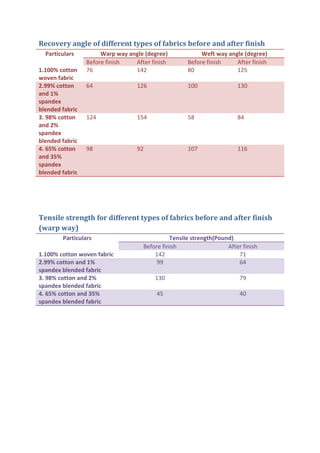
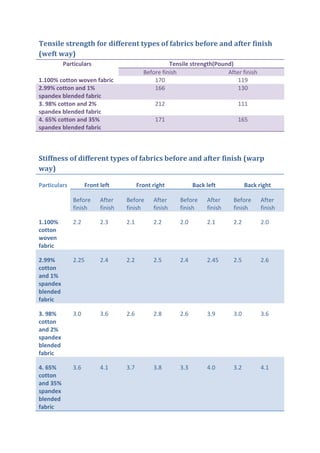
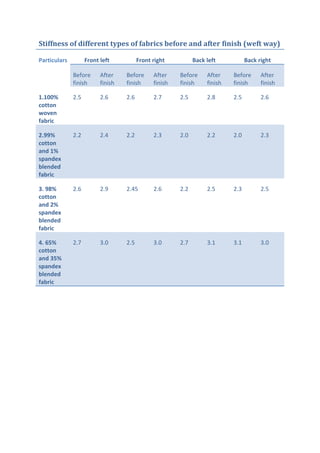
This document discusses wrinkle resistant finishes for fabrics using resin treatments. It describes the mechanism of wrinkle formation in cellulosic fibers and how formaldehyde-based resins can be used to crosslink fibers and reduce hydrogen bonding. The process involves impregnating fabrics with urea-formaldehyde or dimethylol ethylene urea precondensate solutions, curing the treated fabrics, washing and softening. Effects of the finishes on fabric properties like recovery angle, tensile strength and stiffness are analyzed. Recipes for resin treatments of cotton, viscose and polyester fabrics are provided.