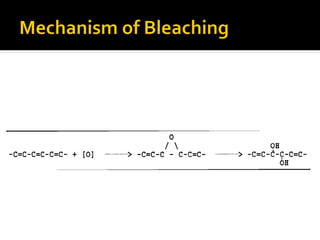
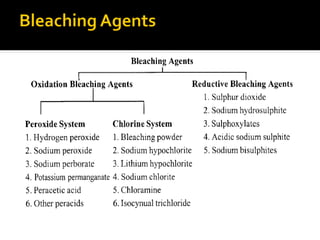
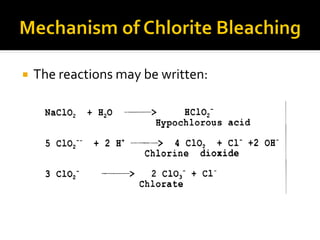
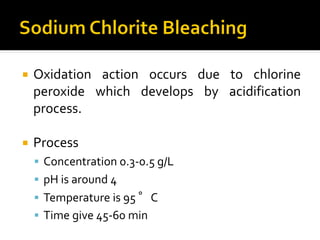
Natural fibers contain coloring compounds that make them appear off-white. The objective of bleaching is to remove these color bodies and produce a white fabric using oxidizing bleaching agents while minimizing fiber damage. Hydrogen peroxide is the most widely used bleaching agent for cotton and blends. It works through its decomposition product, perhydroxyl ion, which breaks the double bonds in color compounds at an optimal pH of 10-11. Proper regulation of perhydroxyl ions through stabilizers prevents rapid decomposition of the bleach and fiber degradation. Temperature, time, concentration, and liquor ratio must be optimized to achieve effective bleaching with minimal impact on strength properties.