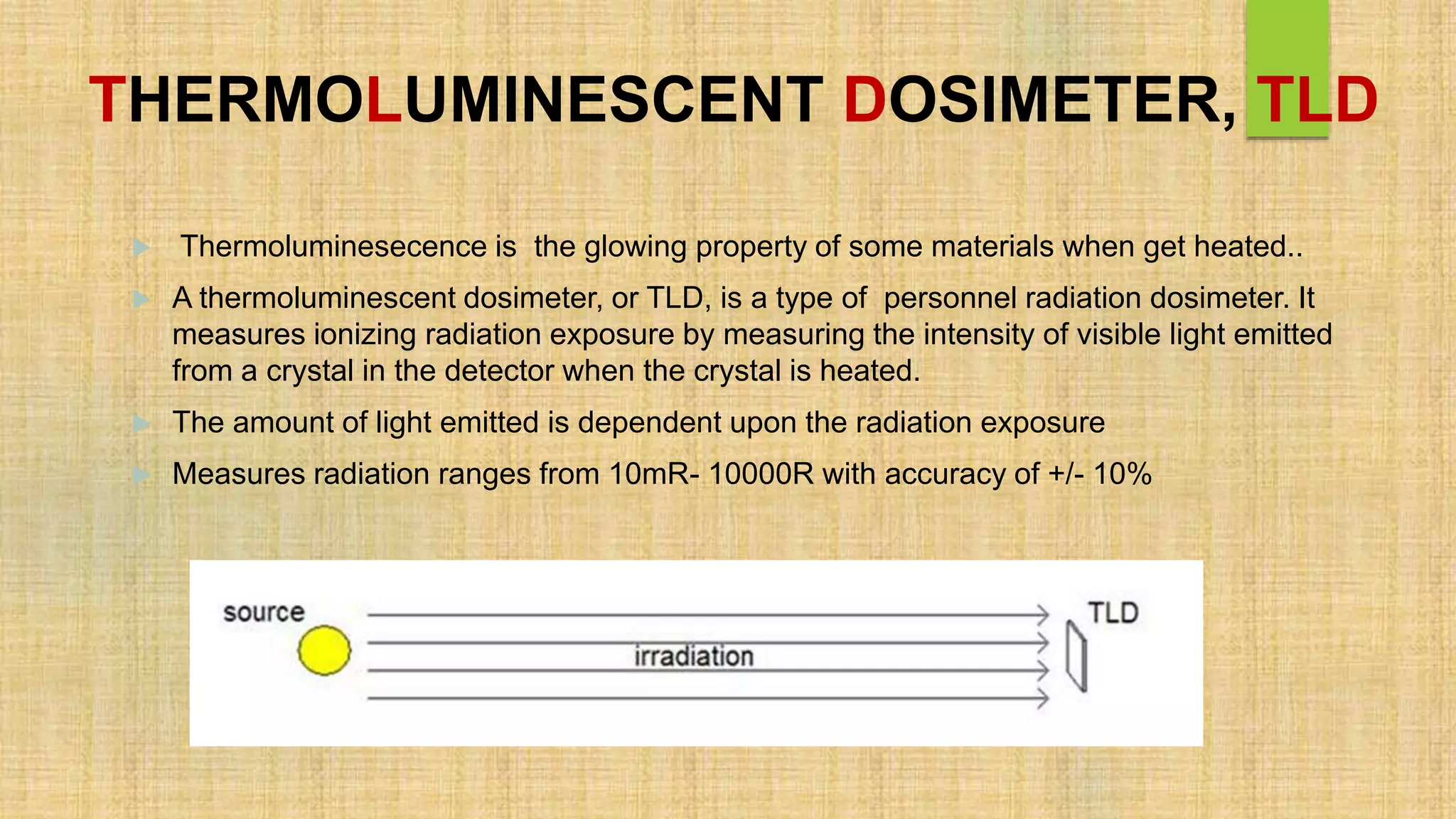
Thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) are used to monitor radiation exposure. TLDs use crystals that emit light when heated, with the amount of light proportional to radiation exposure. Key aspects include:
1) TLDs measure exposure to ionizing radiation like x-rays and gamma rays by heating the crystal and detecting the light emitted using a photomultiplier tube.
2) Common TLD materials include lithium fluoride, calcium fluoride, lithium borate, and calcium sulfate. In India, calcium sulfate doped with dysprosium is commonly used.
3) TLDs are reusable, have good sensitivity and linearity, and allow quick readout of accumulated