1) Investment can be defined as expenditure on capital goods that add to a firm's productive capabilities. It includes purchasing tools, equipment, and other assets.
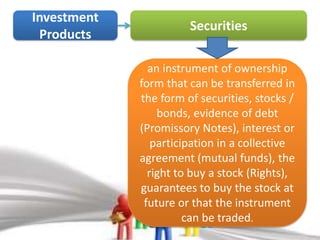
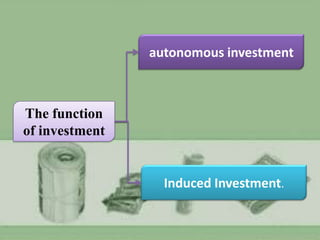
2) Common types of investments include securities like stocks and bonds, autonomous investments made by firms themselves, induced investments in response to other investments, land investments, and educational investments.
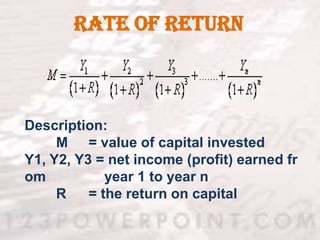
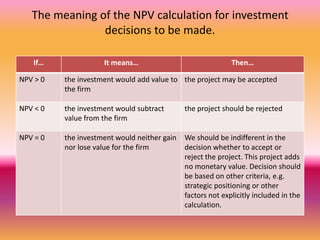
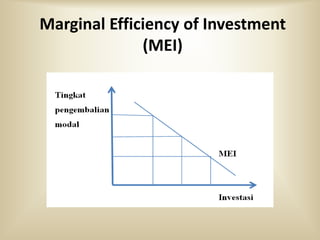
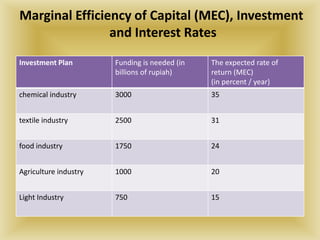
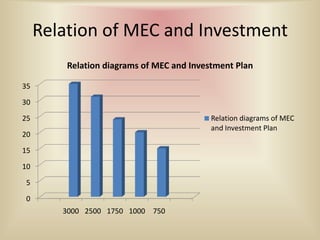
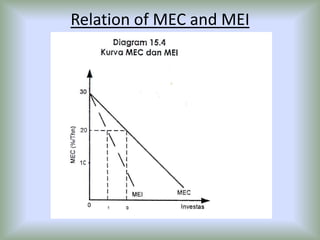
3) When evaluating potential investments, firms consider factors like the expected rate of return, costs of the investment, production assessment methods such as payback period and net present value, and how the investment affects the firm's marginal efficiency of capital and marginal efficiency of investment.