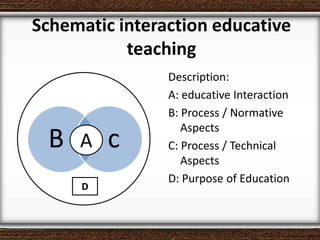
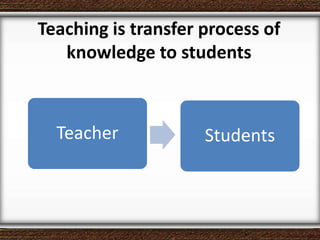
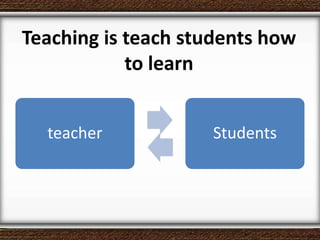
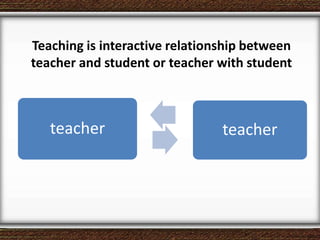
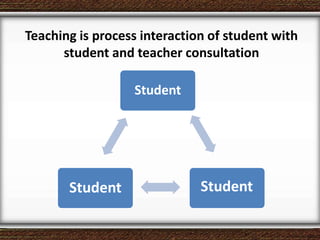
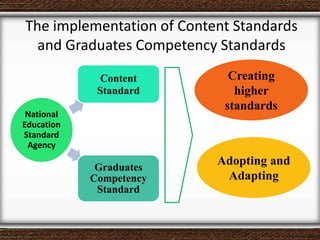
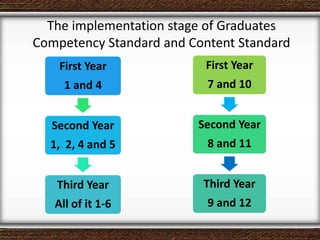
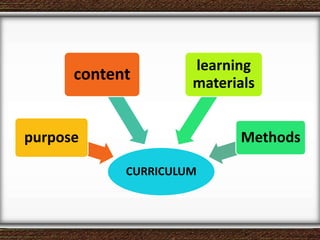
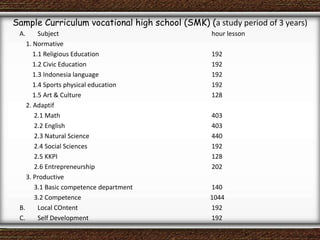
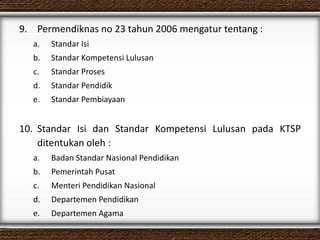
The document discusses the interaction between teachers and students in educational settings, emphasizing that effective teaching and learning processes are guided by set goals, instructional methods, and educational standards. It outlines the roles of teachers and students, the importance of behavioral change through learning, and the structural components of curricula at various educational levels. The document also highlights national education standards and requirements for curriculum development and implementation to achieve educational objectives.