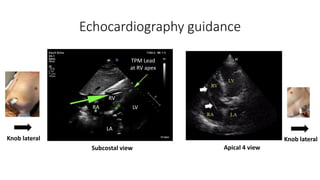
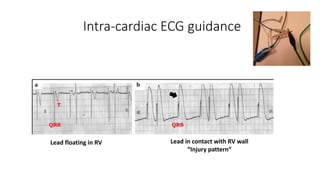
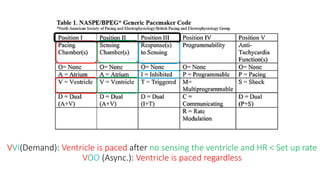
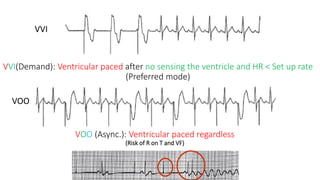
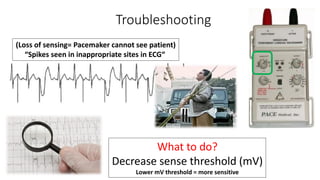
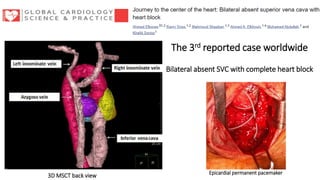
This document discusses how to insert a temporary pacemaker. It begins by providing historical context, noting the first patient to be kept alive for months using a pacemaker device. It then outlines the key steps for inserting a temporary pacemaker, including obtaining venous access, positioning the pacing lead under fluoroscopy or echocardiography guidance, and setting up the pacemaker device. Potential complications are addressed, as well as troubleshooting loss of capture or sensing. Special situations like externalized batteries or congenital vascular anomalies are also covered.